Effective Maintenance Problem Solving Strategies
Effective maintenance problem-solving is a fundamental shift in operational strategy. It involves moving from reactive repairs toward a proactive approach that anticipates failures, reduces downtime, and improves asset reliability.
Instead of only addressing symptoms, this strategy uses data, modern tools, and systematic troubleshooting to identify the root cause of a problem. This transforms maintenance from a cost center into a driver of operational efficiency, extending equipment life and enhancing competitive advantage.
Moving Beyond Break-Fix Maintenance
The traditional "if it ain't broke, don't fix it" mindset is a liability in any industrial setting. This reactive, break-fix model leads to a constant cycle of unplanned downtime and escalating costs, with maintenance teams perpetually addressing emergencies. Emergency repairs are invariably more expensive and disruptive.
Transitioning to a culture of proactive maintenance problem-solving changes this dynamic. Instead of waiting for a breakdown, a proactive team uses data and structured analysis to predict potential failures.
The mindset shifts from asking, "How do we fix this?" to "Why might this fail in the first place?" A key part of this is understanding the core differences between proactive vs reactive maintenance. When a team embraces this change, it stops being a drain on resources and becomes a strategic driver of reliability.
The Value of a Proactive Culture
A proactive culture empowers technicians by encouraging them to identify subtle, leading indicators of failure, such as unusual vibrations, slight temperature changes, or minor dips in performance. This focus on prevention significantly impacts the bottom line by minimizing costly emergency work and maximizing the operational life of critical assets.
Predictive maintenance, a cornerstone of this approach, utilizes advanced AI and IoT technologies to transform how maintenance problems are solved.
A study of 268 European companies found that predictive maintenance can reduce maintenance costs by 12%, increase equipment availability by 9%, and extend the lifetime of aging assets by 20%. The data supports the strategic value of this approach.
This visual breaks down the real-world impact of proactive vs. reactive maintenance, highlighting key metrics like downtime, human error, and repair times.
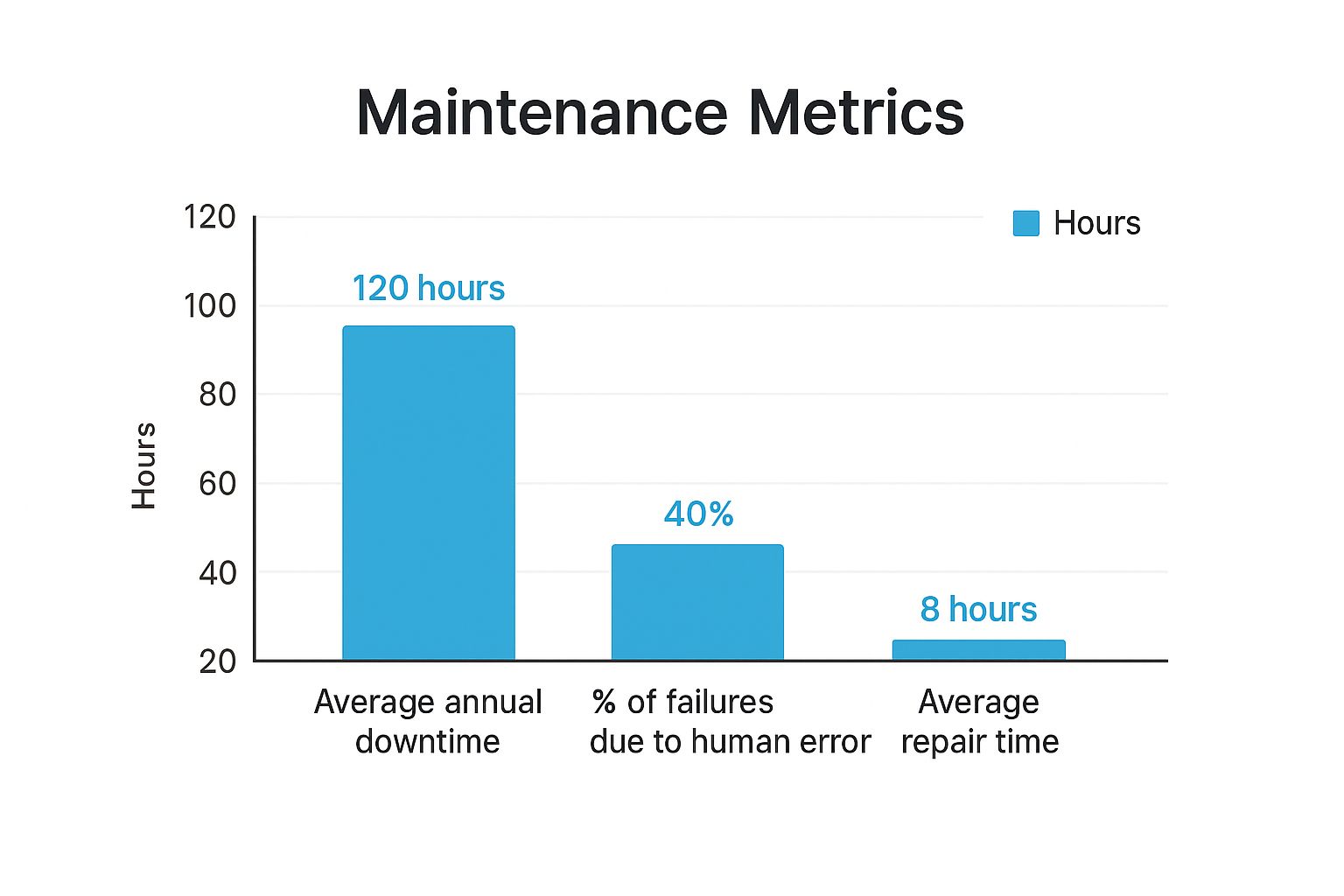
The data makes it clear: a proactive strategy not only reduces downtime and repair times but also mitigates the risk of failures caused by human error.
Why Proactive Strategies Are Essential
Adopting a proactive mindset is essential for maintaining efficiency and competitiveness. It creates a stable, predictable production environment where resources are allocated based on data-driven insights rather than constant crisis management.
A proactive maintenance strategy doesn't just fix problems faster; it prevents them from happening in the first place, turning every potential failure into an opportunity for improvement.
To put it into perspective, here’s a quick breakdown of the mindsets behind each approach.
Reactive vs Proactive Maintenance Mindsets
| Aspect | Reactive Maintenance (Break-Fix) | Proactive Maintenance (Predictive/Preventive) |
|---|---|---|
| Trigger | Equipment failure or breakdown. | Data analysis, scheduled inspections, performance trends. |
| Goal | Restore functionality as quickly as possible. | Prevent failures before they occur. |
| Cost | High, due to unplanned downtime and emergency repairs. | Lower, due to planned work and optimized resource use. |
| Planning | Minimal to none; always in crisis mode. | Strategic; work is scheduled to minimize disruption. |
| Outcome | Unpredictable schedules, lower asset reliability. | Increased uptime, extended equipment life, improved safety. |
Ultimately, this strategic shift away from the "break-fix" cycle leads to several tangible benefits that you can see and measure.
- Reduced Unplanned Downtime: By identifying issues early, teams can schedule repairs during planned shutdowns, keeping production on track.
- Improved Asset Reliability: Continuous monitoring and preventive actions maintain equipment health for longer periods.
- Enhanced Safety: A well-maintained environment is inherently safer, drastically reducing the risk of accidents caused by equipment failure.
A Practical Framework for Troubleshooting

Effective maintenance is a repeatable process, not a matter of luck. When critical equipment fails, the pressure to restore it immediately can lead to rushed judgments and temporary fixes that only address a symptom, not the core problem.
A structured diagnostic framework provides a clear, methodical path from problem identification to a lasting solution. Instead of jumping to conclusions, this approach encourages technicians to think critically. It begins with observation and ends with a verified fix that prevents recurrence. This discipline is what separates a quick patch from a permanent solution.
Observe and Gather Evidence
The first step is to act as an investigator. Before performing any actions, gather as much information as possible about the failure. Consult the operators who were present when it occurred. What did they see, hear, or smell that was out of the ordinary?
Consider a common issue: a conveyor belt that repeatedly drifts out of alignment. The immediate impulse might be to adjust the rollers. However, a professional technician investigates first.
- Check the Logs: Review the maintenance history to see if this has happened before.
- Document Everything: Take photographs or a short video of the belt's current state and any unusual conditions.
- Look for Clues: Is there an abnormal buildup of debris? Have environmental conditions like temperature or humidity changed recently?
This initial data collection provides the necessary context to move forward and prevents premature—and often incorrect—assumptions. You are building a complete picture of the problem before forming a hypothesis.
By treating every equipment failure as a puzzle to be solved with evidence, you move beyond simple repairs and start building a more reliable operation. This foundational step is key to effective maintenance problem solving.
Form a Hypothesis and Test It
With solid evidence in hand, you can form a logical hypothesis. Returning to the conveyor belt example, the data may point to a worn-out pulley bearing rather than a simple tracking issue. This is your educated, testable theory.
Next, test that theory in a controlled and safe manner. This does not require disassembling the entire system. It involves small, targeted actions to prove or disprove the hypothesis. You could carefully inspect the suspected bearing, listen for abnormal noises with a stethoscope, or use a thermal camera to check for overheating.
For complex problems, especially with intricate machinery, having the right resources is critical. A solid guide to industrial electrical repair, for example, can offer specialized knowledge to complement your troubleshooting skills. If your tests confirm the hypothesis, you can proceed with the repair. If not, return to the evidence and form a new theory. This process saves significant time and resources compared to guesswork.
Verify the Solution and Document Everything
After implementing the fix—for instance, replacing the faulty bearing—the job is not complete. The final, critical step is to verify that the solution was effective. Run the conveyor belt under its normal load and observe it closely to ensure the misalignment is permanently resolved.
Equally important is documenting the entire process. Record the symptoms, your hypothesis, the testing method, and the final solution. This creates an invaluable knowledge base for the entire team. This is also where effective training provides significant value; well-documented procedures are ideal material for immersive VR training programs, helping new technicians learn from real-world problems. This disciplined approach ensures every issue makes the entire maintenance operation smarter.
Using Digital Tools for Smarter Diagnostics

The era of maintenance troubleshooting based solely on intuition and experience is over. In today's industrial environments, effective problem-solving hinges on having the right data at the right time. Digital tools bridge this gap, transforming diagnostics from a process of guesswork into a precise, evidence-based science.
Technologies like a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) and Internet of Things (IoT) sensors provide technicians with a significant advantage. They serve as a centralized, digital repository for your entire operation, replacing scattered paper logs and fallible human memory. This shift from speculation to data-driven decisions is what separates a reactive team from a proactive one, allowing you to identify problems earlier and solve them with confidence.
The CMMS: Your Equipment's Digital History
A CMMS acts as a complete, searchable history for every piece of equipment. When a machine malfunctions, a technician can instantly access a detailed log of every past repair, inspection, and parts replacement for that specific asset. This is a game-changer for efficient maintenance problem solving.
For example, if a hydraulic press shows a subtle pressure drop, a technician can consult its CMMS history before touching any tools. They might discover the same issue occurred six months prior and was resolved by replacing a specific seal. This simple check can save hours of diagnostic time and prevent the team from repeating previous efforts.
It is no surprise that CMMS platforms are centralizing workflows on a massive scale. The global market, valued at $1.06 billion, is projected to experience significant growth through 2030 as more organizations leverage data for a competitive edge. You can read more about the CMMS trends reshaping maintenance.
IoT: Your Eyes and Ears on the Floor
While a CMMS provides historical data, IoT sensors offer a real-time view of your machinery's health. These small, smart devices can be attached to critical assets to monitor everything from vibration to temperature.
By integrating real-time data from IoT sensors, maintenance teams can shift from being reactive responders to proactive problem solvers, catching failures before they ever happen.
This continuous stream of data enables you to spot anomalies that would be invisible to the human eye.
- Vibration Analysis: A sensor can detect a minor increase in vibration from a motor, signaling a failing bearing long before it seizes and causes a shutdown.
- Temperature Monitoring: Continuous temperature tracking can alert you to an overheating component, indicating issues like poor lubrication or an electrical fault.
- Pressure and Flow Rates: In fluid systems, sensors can instantly identify a pressure drop or inconsistent flow, pointing directly to a leak or blockage.
When you combine the historical context from a CMMS with live data from IoT sensors, you achieve a complete operational picture. Every decision is backed by solid information, leading to faster, more accurate resolutions.
Boosting Technician Skills with AR and VR
Even the best diagnostic tools are only as effective as the technician using them. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are technologies that amplify human expertise. These tools are fundamentally changing maintenance problem solving by closing critical knowledge gaps and empowering teams directly on the factory floor.
Consider a junior technician facing a complex piece of equipment for the first time. Instead of searching through a manual, they can wear AR glasses. Instantly, digital work instructions, interactive 3D models, and schematics appear overlaid on the real-world machine.
What was once an intimidating task becomes a clear, step-by-step process guided by digital expertise.
On-Demand Expertise from Anywhere
A significant advantage of AR is its ability to provide remote expertise. A top expert can be on another continent and still offer direct, hands-on guidance to a technician on-site. The remote expert sees exactly what the field technician sees through their headset's camera.
From their desk, the expert can annotate the technician’s view in real time—circling the correct valve to turn or drawing an arrow to the next connection point. This "see-what-I-see" support delivers measurable benefits:
- Higher First-Time Fix Rates: With expert guidance, technicians can diagnose and repair issues correctly on the first attempt more often.
- Reduced Travel Costs: Deploying your best minds digitally saves significant travel expenses and eliminates frustrating delays.
- Faster Problem Resolution: An issue that might have caused days of downtime while waiting for an expert to arrive can now be solved within hours.
The practical advantages are clear. We dive deeper into how augmented reality changes maintenance in our dedicated guide. It is like having your most seasoned problem-solver on-site for every critical repair.
Safe Training for High-Stakes Scenarios
While AR enhances the real world, VR creates entirely new, risk-free training environments. VR simulations provide technicians a safe space to practice their response to high-stakes equipment failures. They can learn to troubleshoot a catastrophic engine failure or a critical system shutdown without any danger to themselves or the asset.
By allowing technicians to fail safely in a virtual setting, VR builds the muscle memory and confidence needed to perform flawlessly when it counts in the real world.
This is where true competence is built. A technician who has calmly navigated a simulated hydraulic system failure is far better prepared to manage the real event. This approach accelerates learning and ensures your team is ready for worst-case scenarios, turning potential disasters into manageable maintenance tasks.
Turning Quick Fixes into a Long-Term Strategy

Solving a problem quickly provides immediate relief, but preventing it from recurring delivers long-term value.
This is the core of sustainable maintenance problem solving. It requires a mindset shift from applying an immediate fix to understanding the root cause of the failure. Every repair call becomes an opportunity to improve the resilience of your entire operation.
When you make this pivot, you break the cycle of repeatedly addressing the same issues. Each downtime event becomes a data point, helping you build a robust reliability program for the future.
Finding the Real Why with Root Cause Analysis
When a machine fails, the immediate cause is often just a symptom of a deeper issue. Root cause analysis (RCA) is a method for digging past the surface-level problem to find what is truly happening.
Instead of just replacing a blown fuse and considering the job done, RCA compels you to ask critical follow-up questions. Why did the fuse blow?
Was it a power surge, an overheating motor, or a design flaw in the machine itself? Identifying the true cause is the only way to implement a corrective action that is effective long-term. This investigative approach is fundamental to building any sustainable strategy.
Build a Searchable Knowledge Base
One of the most powerful habits is to document every solution. After a technician resolves an issue, their final step should be to log the entire process—symptoms, diagnosis, and fix—into your CMMS. This simple action creates a searchable, centralized knowledge base that the entire team can utilize.
The benefits are significant:
- Faster Future Repairs: The next time a similar problem occurs, another technician can instantly access the documented solution, saving hours of diagnostic time.
- On-the-Job Training: New hires gain access to a real-world library of problems and solutions, accelerating their familiarity with your specific equipment.
- Pattern Identification: Over time, this data reveals patterns, helping you identify recurring problems and assets that require overhaul or replacement.
This documented history becomes an invaluable asset. This shared knowledge becomes even more powerful when you explore how to use augmented reality for training to bring these documented solutions to life.
By documenting every solution, you turn individual experience into collective intelligence, ensuring that lessons learned are never lost.
Use Data to Refine Preventive Maintenance
Finally, all learnings from troubleshooting should directly inform your preventive maintenance (PM) schedules. If you discover a specific component is consistently failing at nine months instead of the manufacturer-recommended twelve, you can adjust your PMs to address it proactively.
This data-driven approach transforms your maintenance plan from a static document into a dynamic one that adapts to the realities of your operations.
This is more important than ever. The Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) market is valued at approximately $698 billion and is projected to reach $831 billion by 2029, according to ResearchAndMarkets.com. This growth highlights the critical importance of turning every quick fix into a lasting strategic advantage.
Common Questions About Modern Maintenance
Introducing new approaches to traditional maintenance problems naturally raises questions. Teams want to understand the practical implications, from financial justification to gaining adoption from seasoned professionals. Addressing these questions directly is essential for a smooth transition.
The key is to focus on the real value and the human element of implementation. A successful case must demonstrate clear, measurable benefits for everyone, from executive leadership to technicians on the floor.
How Do I Justify the Cost of AR and VR Tools?
The key is to frame the discussion around "investment" rather than "cost." Begin by calculating the real cost of your current problems. Determine the financial impact of one hour of unplanned downtime, including lost production, repeat repairs, wasted materials, and the expense of bringing in senior experts for complex issues.
Once you have this baseline, you can demonstrate how AR and VR directly reduce these costs.
- Improved First-Time Fix Rates: Remote expert guidance via AR can often eliminate the need for secondary or tertiary service calls.
- Reduced Travel Expenses: Calculate the savings from eliminating flights, hotels, and per diems for top specialists. Remote support makes them available anywhere, instantly.
- Faster, Safer Onboarding: VR simulations enable new hires to become proficient more quickly by practicing on complex machinery without real-world risk.
When you present a business case that ties directly to efficiency gains and concrete cost savings, the value becomes undeniable. It is no longer an expense; it is a strategic investment in a more resilient operation.
When leadership can see that the cost of doing nothing is far higher than the investment in new tools, the decision gets a whole lot easier. The ROI isn’t just about dollars saved; it's about building a more skilled, agile, and effective workforce.
What Is the Best First Step to Becoming More Proactive?
Start by using the data you already have. If you aren't collecting data, start now. The foundation of any proactive maintenance strategy is good information. If you are not using a CMMS, implement a basic system and begin logging all maintenance activities: what broke, how it was fixed, and the time it took. This data is invaluable.
Analyze these records to identify your repeat offenders—the machines that fail most often or are most costly to repair. By targeting these high-impact assets first with a focused preventive maintenance plan, you can achieve a quick, measurable win. This early success builds the momentum needed to gain organization-wide support for a more proactive mindset.
How Can We Get Experienced Technicians to Adopt New Technology?
Involve them from the beginning and use the technology to solve a problem they actually face. Do not push technology for its own sake. Identify a daily frustration and demonstrate how a new tool can eliminate it. For example, instead of having them spend 20 minutes searching for a paper manual, provide a tablet with instantly searchable digital versions.
Run a small pilot program with a few receptive technicians. Make their success visible to the rest of the team. When other technicians see their colleagues' jobs becoming easier and less frustrating, they will be more likely to adopt the new tools. It becomes a practical choice, not a top-down mandate. To validate the benefits, it is important to know how to measure training effectiveness to show quantifiable improvements.
At AIDAR Solutions, we build the immersive AR and VR tools that give your maintenance teams the power to solve problems faster and train more effectively. Find out how our solutions can deliver a rapid return on investment for your organization at https://aidarsolutions.com.



Comments(02)