Create a Successful Virtual Reality Training Program Today
For decades, corporate training has relied on established methods like classroom instruction, e-learning modules, and dense manuals. While these methods serve a purpose, they often fail to bridge the critical gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application under pressure.
A virtual reality training program fundamentally changes that dynamic. It is not about passively watching videos or reading instructions. It’s about putting on a headset and stepping directly into a hyper-realistic, interactive environment where users learn by doing. This is a powerful tool for building real-world skills that are retained long-term.
Why VR Is Reshaping Corporate Training
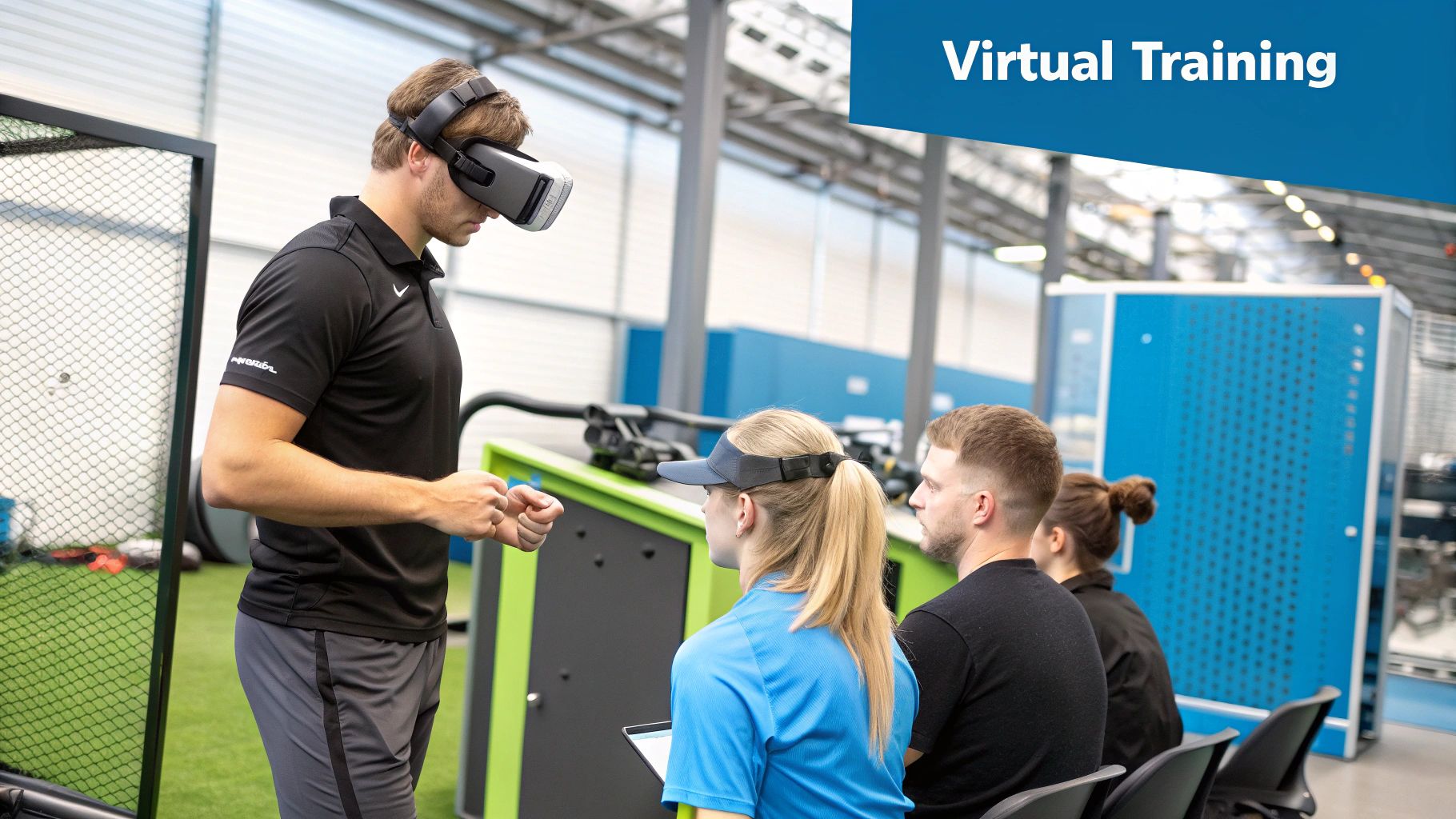

VR training creates a safe, controlled space to tackle complex tasks, make mistakes without consequence, and repeat procedures until they become second nature.
From Theory to Tangible Skills
Imagine a technician learning to service a new, complex piece of machinery. Instead of only reading a manual, they can put on a headset and see a perfect digital twin of that machine. They can walk around it, take it apart, and reassemble it step-by-step. If they make a mistake, they can reset the scenario and try again—with no risk of injury or damage to expensive equipment.
This type of hands-on experience builds muscle memory and situational awareness in a way that passive learning cannot. The result is a workforce that is more confident, capable, and prepared for real-world challenges.
Key Takeaway: The primary strength of a virtual reality training program is its ability to turn passive learners into active participants. When users are physically engaged in the training process, knowledge retention improves significantly.
The numbers support this shift. The global market for virtual reality training is projected to grow from approximately $4.4 billion in 2023 to $28.7 billion by 2030. This substantial growth is driven by proven results, with research indicating that VR can increase learning effectiveness by as much as 76% compared to traditional methods.
To help put these differences into perspective, here's a quick comparison.
VR Training vs. Traditional Methods
| Metric | Virtual Reality Training | Traditional Training |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement | High; fully immersive and interactive. | Low to Moderate; often passive. |
| Retention | High; learning by doing builds muscle memory. | Low; relies on memorization. |
| Safety | 100% safe; simulates hazardous scenarios. | Risky; on-the-job training can lead to accidents. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Higher initial cost, but scalable with low long-term costs. | Lower initial cost, but high recurring costs (travel, instructors). |
| Practice | Unlimited, on-demand practice opportunities. | Limited by resource and instructor availability. |
While traditional methods have a place in a blended learning strategy, VR offers a more robust and effective path to mastery for complex, hands-on skills.
Concrete Applications Across Industries
VR training is proving its value across numerous sectors:
- Healthcare: Surgeons can rehearse delicate operations in a zero-risk virtual operating room. Nurses can practice patient interactions with AI-driven avatars that display a wide range of symptoms and emotional states.
- Manufacturing: Assembly line workers can become proficient with new equipment before it arrives on the factory floor, significantly reducing implementation time and production delays.
- Logistics: New hires can learn to operate a forklift or manage a complex inventory system in a simulated warehouse, dramatically reducing the potential for costly real-world accidents and equipment damage.
These examples demonstrate that VR training is more than a passing trend; it represents a fundamental shift in how organizations empower their teams. To explore the specific advantages further, you can learn more about the benefits of virtual reality training and its direct impact on business outcomes. For more on the latest in corporate learning and technology, the Buddypro blog offers additional insights.
Building Your Strategic Foundation
A successful virtual reality training program begins not with hardware selection, but with a solid strategy. Before any code is written or a virtual environment is rendered, it is essential to define what success looks like. This strategic foundation ensures every decision serves a clear purpose, preventing costly missteps and linking the final product to measurable business goals.
The first step is a practical needs analysis to identify the specific skills, processes, or scenarios where VR can deliver the greatest impact. Not every task is a suitable candidate. Focus on areas characterized by high risk, high complexity, or high stakes, where hands-on practice is critical but too difficult or dangerous to replicate in the real world.
For example, training technicians to service complex machinery is an ideal use case. The equipment is expensive, downtime costs money, and mistakes can cause injury. A virtual reality training program allows them to practice intricate procedures repeatedly in a safe, consequence-free environment.
Defining Clear Learning Objectives
Once the right use case is identified, the next step is to establish clear, measurable learning objectives. Vague goals like "improve technician skills" are insufficient. Objectives must be specific and actionable, serving as the blueprint for the entire program.
Think in terms of what a learner should be able to do after the training.
- Weak Objective: "Understand the new hydraulic press."
- Strong Objective: "Successfully complete the 12-step startup sequence for the Model 7 hydraulic press in under 15 minutes with zero safety violations."
This level of detail dictates everything from the scenario design to the feedback mechanisms built into the VR environment. It also provides a concrete benchmark for measuring success.
A well-defined objective is your project's North Star. It keeps the development team focused, manages stakeholder expectations, and ultimately determines whether your program delivers a real return on investment.
This visual illustrates how these foundational steps connect to the broader project.
As shown, a thorough needs assessment is the crucial first stage, directly influencing the design of the virtual environment and the learner's journey.
Securing Stakeholder Buy-In
A VR training initiative often requires a significant upfront investment, making stakeholder buy-in essential. Key stakeholders may include department heads, finance managers, IT leaders, and the frontline supervisors whose teams will use the training.
To gain their support, it is important to communicate the benefits in terms they understand.
- For Finance: Present a clear ROI projection. Discuss reductions in equipment damage, travel costs for trainers, and employee downtime.
- For Operations: Highlight tangible improvements, such as a 25% reduction in onboarding time or a 50% decrease in safety incidents.
- For IT: Discuss the technology's scalability and its potential for integration with existing Learning Management Systems (LMS).
Frame the value proposition with compelling examples. Explain how a VR scenario can prevent a $20,000 repair bill caused by a single mistake or help avoid a serious safety incident. This makes the potential return on investment clear and immediate.
Mapping the Learner Journey
Finally, map out the entire experience from the trainee's perspective to ensure the journey is intuitive, engaging, and effective. For the technician example, a typical journey might look like this:
- Onboarding: The user begins in a simple, safe "virtual lobby." Here, they become comfortable with the VR controllers and basic movement without the pressure of the main task.
- Guided Practice: The user is transported to the virtual machine. A voiceover and visual highlights walk them through the 12-step startup sequence for the first time.
- Independent Assessment: The aids are removed, and the user must perform the entire sequence from memory. The system tracks their time, accuracy, and any safety violations.
- Feedback and Review: After completion, the user receives a detailed performance report. They can even watch a replay of their actions from a third-person perspective to identify areas for improvement.
This structured journey builds confidence progressively. By thinking through each stage, you transform a list of objectives into a cohesive and impactful virtual reality training program that delivers measurable results.
Designing Effective Immersive Content

This is where planning and analysis translate into a tangible experience. Designing content for a virtual reality training program requires a blend of art and science, demanding a deep understanding of human learning principles, not just technology.
The goal is not novelty, but the creation of scenarios that build genuine muscle memory and forge critical, lasting skills.
Effective VR is not about building a pixel-perfect replica of the real world. It is about engineering a focused learning environment where every element, from lighting to background noise, serves a specific purpose. The true value emerges from realistic scenarios that compel trainees to apply their knowledge under pressure, cementing skills more effectively than passive observation.
Mastering Instructional Design for VR
Instructional design in a virtual environment operates under a different set of rules. Unlike a webpage or video with a fixed frame, a VR environment is all-encompassing, requiring active guidance of the learner's attention. Without clear cues, a user can easily become distracted or miss vital information.
Effective experiences are built around a few core VR-specific principles:
- Guided Attention: Use visual and auditory cues to direct focus. A subtle glow on a critical lever, a specific sound signaling a machine malfunction, or a highlighted path ensures the user is looking where they need to be.
- Real-Time Feedback: This is one of VR’s most powerful features. If a trainee makes a mistake, the system should provide instant, constructive feedback, such as a visual warning, an audio alert, or haptic feedback through the controllers. This creates a powerful learning loop.
- Progressive Scaffolding: Build skills incrementally. Start with a guided walkthrough, then remove some aids to allow for practice, and finally, present a full assessment where the user must perform the entire task independently.
The quality of the training software itself is a critical factor. The VR training simulator software market is a specialized field projected to grow from USD 0.53 billion in 2024 to USD 1.7 billion by 2034. This growth indicates the strong demand for sophisticated platforms capable of delivering these nuanced and effective learning experiences.
Choosing Your Immersive Path
When creating content, you face a key decision: 360-degree video or a fully interactive CGI simulation. The right choice depends on your learning goals, budget, and the required level of hands-on interaction.
Key Insight: The choice between 360-degree video and interactive CGI is not about which is "better," but about selecting the right tool for the task. Aligning the technology choice with specific training goals is essential for maximizing impact and ROI.
360-degree video is excellent for placing a learner inside a real-world location, allowing them to look around as if they were physically present. This method is effective for situational awareness training, virtual facility tours, or observing an expert perform a task. It is also relatively quick and cost-effective to produce. However, interaction is typically limited to looking around and clicking on hotspots.
The Power of Full Interaction
In contrast, fully interactive simulations built with computer-generated imagery (CGI) offer a much deeper level of engagement. In these environments, trainees can physically grab tools, operate complex machinery, and interact with objects and virtual characters. This is the gold standard for procedural training, complex problem-solving, and any task requiring fine motor skills.
Here’s a quick breakdown to help guide your decision:
| Feature | 360-Degree Video | Fully Interactive Simulation |
|---|---|---|
| Interactivity | Low (look-around, simple clicks) | High (grab, manipulate, operate) |
| Use Case | Situational awareness, virtual tours | Procedural tasks, skill-based training |
| Realism | Photorealistic visuals | Can be realistic or stylized |
| Cost & Time | Lower cost, faster to produce | Higher cost, more development time |
| Best For | Soft skills, observation | Hard skills, muscle memory |
For complex scenarios like emergency response drills or surgical training, an interactive simulation is virtually non-negotiable. If you're looking to develop these kinds of powerful custom programs, exploring our virtual reality training solutions can provide a clearer picture of what is possible.
The Importance of Sound Design
Finally, do not overlook audio. It is often an afterthought but is absolutely critical for true immersion. Realistic sound design grounds the user in the virtual space and enhances the authenticity of the experience.
The clang of a dropped tool, the low hum of active machinery, or the specific beep of a system failure are details that contribute to cognitive buy-in. Beyond recording custom audio, utilizing sources for free sound effects can provide a rich library to bring your virtual world to life.
Choosing the Right Hardware and Partners
Once the training content is mapped out, the next step is to select the technology that will bring it to life. The hardware and partners you choose are as crucial as the scenarios themselves, directly impacting user adoption, scalability, and final ROI.
It is easy to get lost in the array of available hardware, but the choice primarily comes down to one core question: do you need standalone or PC-tethered VR?
Standalone VR headsets are self-contained devices with built-in processors, batteries, and tracking. They offer complete freedom of movement and are simple to set up and manage, making them ideal for large-scale rollouts or training that requires mobility.
PC-tethered VR headsets, in contrast, connect to a powerful computer. This connection allows them to render higher-fidelity graphics and handle more complex simulations. They are the perfect fit for high-stakes training where visual detail is paramount, such as practicing intricate surgical procedures or exploring detailed engineering models.
Aligning Hardware to Training Needs
The "best" hardware is always the hardware that is right for your specific use case.
Consider a logistics company training new forklift operators in a large, open warehouse. Standalone headsets are the clear choice. The freedom from cables is not just a convenience; it is essential for creating a realistic and safe training environment.
Now, imagine an aerospace firm teaching engineers to assemble a complex jet engine. The graphical horsepower of a PC-tethered system becomes non-negotiable to accurately render thousands of intricate parts.
Expert Tip: Do not simply choose the newest headset on the market. Instead, focus on the right headset for your virtual reality training program. Evaluate practical factors like battery life, controller ergonomics, and the ease of managing a fleet of devices.
Getting this right is increasingly important. The immersive training market is projected to climb from USD 16.4 billion in 2024 to nearly USD 69.6 billion by 2030. You can explore the drivers behind this growth in this comprehensive market analysis.
Off-the-Shelf Platform vs. Custom VR Development
Next is the software decision. You have two main paths: using an existing, off-the-shelf (OTS) platform or commissioning a completely custom-built solution. Neither is inherently superior; they serve different needs.
This table breaks down the key differences to help you decide.
Off-the-Shelf Platform vs. Custom VR Development
| Factor | Off-the-Shelf Platform | Custom Development |
|---|---|---|
| Speed to Deploy | Fast; ready to use almost immediately. | Slower; requires a full development cycle. |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, often subscription-based. | High upfront investment. |
| Customization | Limited; works within the platform's features. | Unlimited; built to your exact specifications. |
| Specificity | Best for general skills (e.g., public speaking). | Essential for proprietary or unique processes. |
| Scalability | Generally easy to scale user base. | Scalability must be built into the architecture. |
An OTS platform can be an excellent entry point, especially for training common soft skills or standard safety protocols. However, when you need to teach someone how to service proprietary machinery, a custom solution is often the only way to achieve the required specificity. This is common in specialized fields; for example, you can learn more about how the automotive industry trains employees in virtual reality using bespoke solutions.
Vetting Your Development Partner
If you choose the custom route, selecting the right development partner is paramount. This is a long-term relationship, not a simple transaction. You need a team that understands both the technology and the principles of effective instructional design.
When vetting potential vendors, ask detailed questions:
- Process: "Walk me through your entire development process, from discovery to post-launch support."
- Experience: "Can you show me projects you've completed that are similar to ours in complexity and learning goals?"
- Team: "Who, specifically, would be on our project team? What is their background in corporate training and our industry?"
- Support: "What does your support and maintenance plan look like after we go live?"
A strong partner will act as a consultant, pushing back on ideas that may not align with learning objectives and offering creative solutions. They will be transparent, honest, and enthusiastic about their work. Choosing wisely here is what transforms your vision for an effective virtual reality training program into a real, impactful tool for your team.
Deploying and Measuring Your Program

This is the phase where all your careful planning and design work comes to fruition. Transitioning from a development project to a live virtual reality training program is a critical stage that will determine user adoption and the program's long-term success.
A smooth rollout is more than simply activating the system; it requires a deliberate, phased approach. An effective strategy begins with a pilot test. Before a company-wide launch, a small, representative group of end-users should run through the entire program. This is not just for bug-finding; it is the best opportunity to gather candid, real-world feedback on everything from the user interface to scenario difficulty.
This initial feedback is invaluable. The best deployments have built-in mechanisms to understand how to get customer feedback directly from participants. This allows for crucial adjustments before a full-scale launch.
Mastering the Logistics of Rollout
After integrating pilot feedback, you can prepare for wider deployment. This involves managing the logistics of hardware, user onboarding, and technical support. A clunky user experience can undermine even the most well-designed content.
- Hardware Management: Implement a clear system for storing, charging, and sanitizing headsets. A dedicated, secure charging station is non-negotiable. For larger rollouts, a simple check-in/check-out system helps track device allocation.
- User Onboarding: The first five minutes in VR are crucial. Create a standardized onboarding session where a trainer helps users fit the headset properly, learn the controllers, and acclimate in a low-pressure "welcome" environment before starting the training.
- Technical Support: Establish a clear point of contact for technical issues. Whether it is an in-house expert or a dedicated support line from your development partner, users need to know who to call for help.
This structured approach transforms deployment from a potential challenge into a streamlined process, setting the stage for strong user adoption and positive first impressions.
Defining Your Key Performance Indicators
With your program live, the focus shifts from implementation to impact. To prove the value of your investment, you must measure what truly matters, looking beyond simple completion rates. This means tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) designed specifically for the immersive experience.
Traditional e-learning metrics like "time spent in module" are less relevant here. Instead, focus on data that reflects genuine skill acquisition and behavioral change. While a VR training program is powerful, it is also useful to compare its effectiveness with other immersive technologies. For more information, you can explore our insights on using augmented reality for training to see how different tools can complement each other.
Key Takeaway: The data collected from a VR program is its secret weapon. It provides objective, granular insight into employee performance that is nearly impossible to obtain from traditional training. This data forms the bedrock of your business case.
Measuring What Matters Most
Your KPIs should tie directly back to the learning objectives established in the strategy phase. The right metrics provide hard evidence of your program's effectiveness and its contribution to the bottom line.
Here are the most impactful KPIs for a virtual reality training program:
| KPI Category | Specific Metrics to Track | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| In-Simulation Performance | • Error rates on specific tasks • Adherence to safety protocols • Accuracy of procedural steps |
This is your most direct measure of skill. It shows if users can actually perform the task correctly and safely inside the simulation. |
| Time-to-Competency | • Number of attempts to pass • Total time to reach proficiency |
This metric screams efficiency. A lower time-to-competency means faster onboarding and a quicker path to productivity for your team. |
| Skill Retention | • Performance scores on re-assessment • Comparison of scores over time |
This proves the training actually sticks. By re-testing users weeks or months later, you can show that VR-acquired skills are retained long-term. |
Translating Metrics into Clear ROI
The ultimate goal is to connect these KPIs to real business outcomes and demonstrate a clear return on investment (ROI). This is how you secure budget for future initiatives and expand the program's reach.
Build a powerful ROI story by linking your VR data directly to operational improvements:
- Reduced Errors: Correlate a drop in in-simulation errors with a real-world decrease in equipment damage or product defects.
- Increased Safety: Show how perfect scores on virtual safety drills lead to a measurable reduction in on-the-job incidents and near-misses.
- Improved Efficiency: Connect your faster time-to-competency metrics with lower employee onboarding costs and getting people into revenue-generating roles sooner.
By collecting and analyzing this performance data, you change the conversation from "training is a cost center" to "this program is a profit driver." You create a data-backed narrative that proves your virtual reality training program is building a more competent, efficient, and safer workforce.
Got Questions About VR Training? We've Got Answers.
As you consider bringing immersive learning into your organization, it is natural to have practical questions. Understanding the specifics—cost, potential roadblocks, and how to prove its value—is key to moving forward with confidence.
Let's address some of the most common questions from teams starting their VR journey.
How Much Does a Virtual Reality Training Program Actually Cost?
The cost of a virtual reality training program can vary significantly based on its complexity and interactivity.
A simple program using 360-degree video might cost a few thousand dollars. However, a fully interactive, custom-built simulation with branching decision paths and multiple scenarios could range from $50,000 to over $300,000. The primary cost drivers are:
- Content Complexity: The level of realism required for the virtual environment.
- Level of Interactivity: The extent to which users manipulate objects and make decisions.
- Hardware: The cost of headsets and any supporting PCs or equipment.
- Development Approach: Using a ready-made platform versus commissioning a bespoke build.
It is important to view this as an investment rather than a cost. The right program pays for itself through improved safety, fewer expensive mistakes, and a more efficient workforce.
What Are the Biggest Hurdles to Getting Started?
The most significant challenges are often related to people and logistics rather than technology. The first major hurdle is typically securing budget and obtaining genuine buy-in from leadership. Following that are the practical logistics of hardware management, including storage, charging, and sanitation protocols.
You might also encounter some initial user hesitation or need to address concerns about motion sickness (though modern headsets have greatly reduced this issue). Perhaps the most critical challenge is creating content that is an effective teaching tool. Designing an experience that is more than a novel demo requires specialized instructional design skills.
Pro Tip: A pilot program is an invaluable tool. By starting small and testing with a limited group, you can resolve logistical and usability issues on a manageable scale before a full deployment, ensuring a smoother final rollout.
How Do You Actually Measure the ROI of VR Training?
Proving the value of VR training comes down to tracking specific metrics that tie directly to business goals. This requires moving beyond simple completion rates to demonstrate real-world impact.
The best way to build your case is to capture performance data from before and after the VR program is implemented. Focus on tangible results such as:
- A quantifiable reduction in training time and faster onboarding for new hires.
- A measurable decrease in on-the-job accidents or costly operational errors.
- A noticeable improvement in productivity or work quality.
- A reduction in costs associated with previous training methods, such as travel, physical materials, or equipment downtime.
By connecting training data to these business outcomes, you can build a powerful case that clearly shows the financial and operational benefits your virtual reality training program is delivering.
Ready to see how a custom VR program could solve your company's unique training challenges? The team at AIDAR Solutions are experts in designing and deploying immersive training experiences that deliver measurable results. Discover our solutions today.


