Manufacturing Process Automation: Boost Efficiency and ROI
Imagine a factory floor that doesn’t just react to problems, but anticipates them. A place where machines communicate and production lines adapt on the fly. This isn't a far-off concept; it's the reality of modern manufacturing process automation.
This is about much more than deploying robots on an assembly line. It's about weaving together digital tools, smart equipment, and a skilled workforce into a single, cohesive system—all aimed at hitting peak performance.
What Is Smart Manufacturing Automation
At its core, manufacturing process automation is the strategic use of technology to control and monitor how products are made and delivered. It's a significant leap beyond simple mechanization. We're talking about creating an interconnected system where machines, software, and people are all on the same page, working in unison.
Think of it less as replacing human effort and more as amplifying it. Automation frees up your team from the repetitive, physically draining tasks, letting them focus on what humans do best: innovation, problem-solving, and quality control.
This approach is the ideal answer to today’s biggest challenges—rising operational costs, stubborn labor shortages, and the relentless demand for higher precision. By automating the right workflows, you can build a production environment that's not just efficient, but also far more resilient and agile.
The Core Components of Automation
Smart automation boils down to three pillars working together. Once you understand how they connect, you can start to picture what a truly modern factory looks and feels like.
- Intelligent Equipment: This is the hardware on the ground. It includes everything from industrial robots handling welding and materials to advanced sensors pulling real-time data right off the production line.
- Digital Tools: This is the brains of the operation. Software like SCADA and DCS acts as the central nervous system, monitoring every process. Meanwhile, AI and machine learning algorithms are crunching the data to predict maintenance needs or find ways to tweak workflows for better output.
- A Skilled Workforce: Automation doesn’t replace people; it elevates their roles. Your team becomes the managers, maintainers, and optimizers of these complex systems. They are supported by powerful tools like Augmented and Virtual Reality for training and remote support.
The real goal of manufacturing process automation isn’t just to make things faster. It's to make them smarter. You're creating a self-optimizing environment where data drives every decision, quality is always improving, and efficiency becomes your biggest competitive edge.
When these three components click, the entire operation flows seamlessly. For example, an IoT sensor might detect a minor, abnormal vibration in a machine and automatically trigger a maintenance alert. An AR-equipped technician can then see expert guidance overlaid directly onto their view of the machine, letting them fix the issue long before it ever causes downtime.
It’s this proactive, data-driven approach that separates smart automation from older methodologies. For any operational leader looking to boost quality and bulletproof their supply chain, it's no longer just an option—it’s essential.
Understanding The Core Automation Technologies
To fully grasp manufacturing process automation, you have to understand the building blocks. These core technologies are the gears, circuits, and brains that make a modern factory tick, each playing its own part in creating a smooth, interconnected operation.
Think of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Distributed Control Systems (DCS) as the factory's nervous system. These are the rugged, reliable workhorses on the plant floor, built to execute precise, high-speed commands for specific machines or entire processes. They’re programmed to handle repetitive tasks with near-perfect reliability, whether that’s controlling a single robotic arm or managing a complex chemical reaction.
Sitting one level above them is the Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system. If PLCs and DCS are the nerves, SCADA is the central command center. It gives operators a high-level, real-time graphical view of the entire operation, pulling data from all the different controllers and displaying it on one screen. This is what allows a single person to monitor production, manage alarms, and make smart decisions from a central hub.
The Key Players In A Smart Factory
Beyond these foundational control systems, a suite of specialized technologies brings new capabilities to the factory floor. Each one tackles a specific challenge, from quality control to materials handling, contributing to a smarter, more efficient production line. Understanding technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a must for any modern manufacturer.
This concept map shows how automation pulls together digital tools, smart equipment, and a skilled workforce into one cohesive strategy.
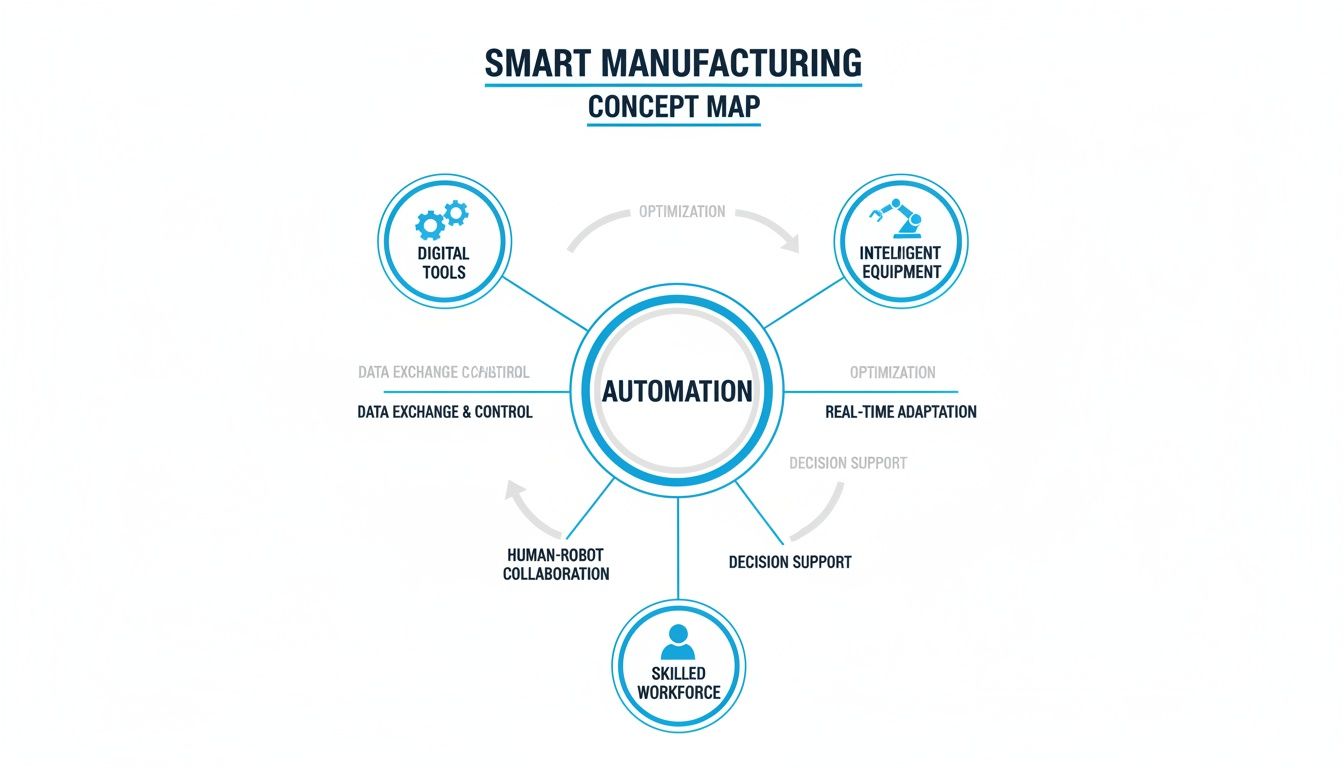
The key takeaway here is that successful automation isn't just about the machines. It’s a balanced approach where technology empowers a well-trained team.
Let's break down some of the most important technologies you'll encounter.
- Industrial Robotics: These are probably the most visible form of automation. Built for strength, speed, and precision, robots are perfect for repetitive and physically demanding jobs like welding, painting, assembly, and packaging. They operate 24/7 without fatigue.
- Machine Vision: This technology gives machines the ability to "see." Using cameras and intelligent software, vision systems can spot tiny defects on products, guide robots with incredible accuracy, and read barcodes at high speed. It's how you build quality control directly into the production line.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT involves embedding sensors into machinery to collect massive amounts of real-time data. These sensors monitor everything from temperature and vibration to energy use, providing the raw information needed to identify and fix problems.
To see how these pieces fit together, the table below outlines the core technologies and what they do on the factory floor.
Key Automation Technologies and Their Roles
| Technology | Primary Function | Manufacturing Application Example |
|---|---|---|
| PLC / DCS | Direct, real-time control of machinery and processes. | A PLC operates a conveyor belt, starting and stopping it with precise timing. |
| SCADA | Centralized monitoring and high-level control of the entire plant. | An operator uses a SCADA dashboard to monitor output from three separate production lines. |
| Industrial Robotics | Automating physical tasks requiring strength, speed, and repetition. | A six-axis robotic arm welds car door frames on an assembly line. |
| Machine Vision | Performing visual inspections and guiding automated equipment. | A camera system inspects bottles for cracks or incorrect fill levels, rejecting defective ones. |
| IoT Sensors | Collecting operational data from equipment and the environment. | A sensor on a motor tracks vibrations to predict when maintenance will be needed. |
| AI / Machine Learning | Analyzing data to predict outcomes and optimize processes. | An ML algorithm analyzes sensor data to adjust machine settings for better energy efficiency. |
Each of these technologies is powerful on its own, but their true value is unlocked when they work together as part of a larger, intelligent system.
Data, Intelligence, And Deployment Models
The real value emerges when all that data is turned into actionable insight. This is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) step in. By analyzing the data streaming in from IoT sensors, AI algorithms can predict when a machine is about to fail, spot subtle bottlenecks in a workflow, or even automatically tweak production settings to improve quality.
This synergy is what makes modern automation so powerful.
Finally, how you deploy these systems is a critical decision. Choosing between on-premise and cloud-based systems depends on your needs for security, scale, and access.
On-premise deployments, which currently dominate the market at $14.9 billion, give you maximum control over your data. This makes them the go-to for sensitive sectors like aerospace and defense. Cloud systems, on the other hand, offer unbeatable flexibility and remote access, making it easier to scale up and collaborate.
The global factory automation market was valued at USD 140.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to nearly double to USD 281.9 billion by 2030, with the automotive and electronics sectors leading the charge. This explosive growth shows just how crucial control systems like PLCs, DCS, and SCADA are for gaining real-time control in demanding environments. Together, these technologies are building a powerful, intelligent ecosystem that is reshaping the future of manufacturing.
The Tangible Business Benefits of Automation
Let's move past the complex technology and system diagrams for a moment. The real story of manufacturing process automation is told on the factory floor and the balance sheet. When you invest in automation, you’re not just buying new equipment; you're making a strategic move that delivers real, measurable returns across your entire operation. These benefits stack up quickly, creating a stronger, more competitive business.
The global rush toward automation isn't just a trend—it's a clear signal that the financial and operational upsides are too big to ignore. The market is expected to rocket from USD 12.28 billion in 2023 to USD 23.96 billion by 2030, all fueled by Industry 4.0 adoption. As you can see from the latest analysis by Grand View Research, companies are using automation to get ahead of rising costs and shaky supply chains.
Boosting Production and Slashing Costs
One of the first things you'll notice after implementing automation is a significant jump in production throughput. Automated systems can run 24/7 without fatigue, hitting a pace and level of precision that human labor simply can't sustain. More output means more products shipped and, ultimately, more revenue.
Consider this: a facility using robotic arms might increase its output from 100 units an hour to 150. That 50% increase doesn't just help meet higher demand; it drops the cost-per-unit substantially.
At the same time, automation optimizes resource usage.
- Less Material Waste: Precision systems make perfect cuts every time, which means significantly less scrap.
- Lower Energy Bills: Smart sensors and AI can power down machines the second they're not needed, leading to serious energy savings.
- Smarter Labor Allocation: Automation takes over repetitive, monotonous jobs, freeing up your skilled workers for higher-value roles where they can make a real difference.
Understanding these cost reductions is the first step in making your business case. If you're ready to start crunching the numbers, our guide on how to calculate return on investment is the perfect place to start.
Elevating Quality and Enhancing Safety
Producing more products is great, but only if the quality holds up. This is where automation is a true game-changer. Automated systems, especially those using machine vision, perform quality checks with relentless consistency. They can spot microscopic defects the human eye would miss, guaranteeing that every single product meets your exact standards.
The result is a steep drop in defect rates, which means fewer costly recalls, less rework, and more satisfied customers.
With automation, manufacturers can finally get out of the reactive "find and fix" quality-control trap. Instead, the system becomes proactive, flagging potential issues in real-time before they ever turn into expensive problems.
On top of that, automation makes the workplace fundamentally safer. Robots take on the jobs that are dangerous, repetitive, or grueling for people—such as handling hazardous chemicals, working in extreme temperatures, or performing constant heavy lifting. This directly cuts down on workplace accidents and injuries, leading to fewer workers' compensation claims and a more secure, engaged team. Exploring the wider benefits of Artificial Intelligence for business management is a great next step, as AI is often the brains behind these advanced safety and quality systems.
Closing the Skills Gap with Immersive Training
The move toward advanced manufacturing process automation is a massive leap forward, but it brings a major challenge with it. These sophisticated systems demand an equally sophisticated workforce to run, troubleshoot, and maintain them. This is where the skills gap appears—and it’s a gap that can catch businesses unprepared.
There's a powerful way to bridge that gap. Immersive training, powered by Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR), takes learning off the page and puts it directly into a hands-on, digital world. It’s about building true mastery before anyone even steps onto the factory floor.
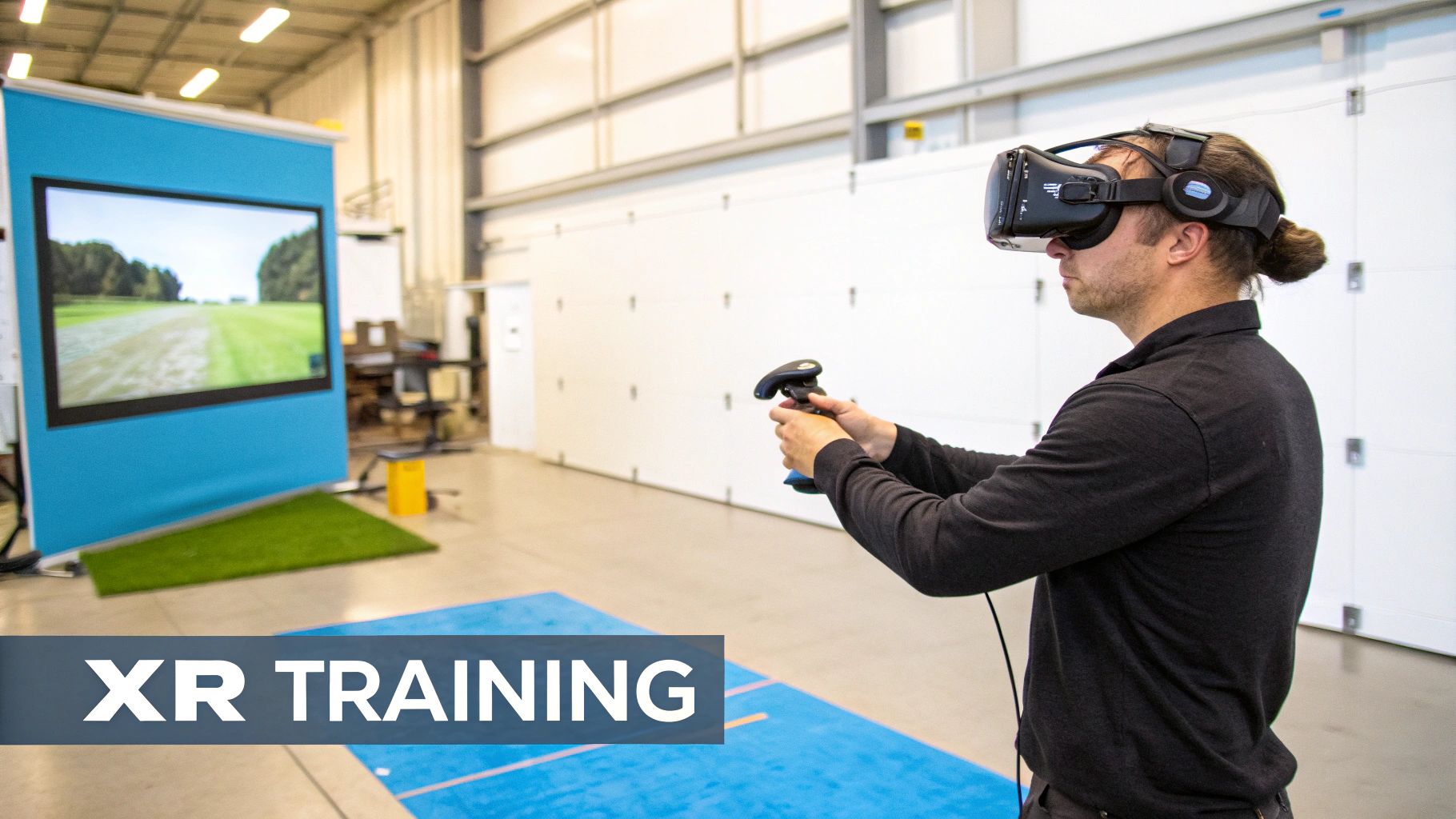

This isn’t just a new training method; it’s a fundamental shift in how people learn and retain critical knowledge. By arming your team with these tools, you empower them to become experts on the very automation that’s driving your business.
Creating Experts in a Virtual World
Virtual Reality (VR) training drops your team into a photorealistic simulation of your actual facility. Inside this digital twin, they can practice commissioning a new robotic cell, programming a complex sequence, or diagnosing a tricky fault—all without risking injury or damaging expensive equipment.
Consider a new technician learning to troubleshoot a complex conveyor system. In VR, they can:
- Practice Complex Procedures: They can run through startup and shutdown sequences dozens of times, building the muscle memory that only comes from repetition.
- Experience Rare Malfunctions: The simulator can replicate high-stakes, low-frequency problems—like a critical sensor failure—that are impossible to safely train for on a live production line.
- Learn Through Failure Safely: If they make a mistake, there's no costly downtime or broken machinery. It’s a learning moment where they can reset and try again until they get it right.
This goes beyond watching a video or reading a manual. It builds deep, practical knowledge by letting people learn by doing.
By immersing teams in a safe, controlled virtual environment, you can accelerate learning curves significantly. This approach completely eliminates material waste from training exercises and removes the production pressure that often hinders effective learning.
The number of industrial robots in operation globally is skyrocketing, and skilled operators and maintenance crews are more critical than ever. With many leaders expecting these new skills to be learned on the job, the need for safer and faster training methods is urgent. Immersive VR training allows workers to learn robot programming and maintenance in lifelike simulations, helping to reduce the need for expert travel and accelerate competency.
Building Confidence and Reducing Risk
One of the biggest benefits of immersive training is confidence. When a technician has already handled a simulated emergency or performed a complex repair multiple times in VR, they approach the real machine with competence and calm. That confidence is crucial for minimizing human error, which remains a leading cause of industrial accidents and downtime.
This training model is also incredibly scalable and consistent. A best-practice procedure developed by your top engineer can be turned into a VR module and deployed to your entire global workforce. Suddenly, everyone is getting the exact same high-quality instruction. That consistency is key to maintaining operational excellence across different shifts, facilities, and even continents.
This isn’t just about teaching skills; it's about creating a culture of preparedness. If you're looking to dive deeper into this, you can explore how augmented reality for training is helping companies build more capable teams. When you give your employees the best tools to learn and grow, your automation investment transforms into a real, sustainable advantage.
How AR Remote Support Transforms Maintenance
Once your automated systems are running, keeping them that way becomes the number one priority. Uptime is everything. Even the most sophisticated automation needs expert maintenance, and every minute a machine is down, it costs money. This is where modern support solutions completely change the game, protecting your investment and keeping the production line moving.
Picture this: a technician is on the factory floor, facing a complex fault in a robotic arm. Traditional support involves a frustrating chain of phone calls, confusing emails, and—often—waiting hours or even days for a specialist to arrive on-site. That downtime is a massive productivity killer and a huge operational expense.
Augmented Reality (AR) remote support offers a much smarter alternative. Instead of waiting, the on-site technician can instantly connect with an expert anywhere in the world, sharing their exact point of view through a tablet or a pair of smart glasses.
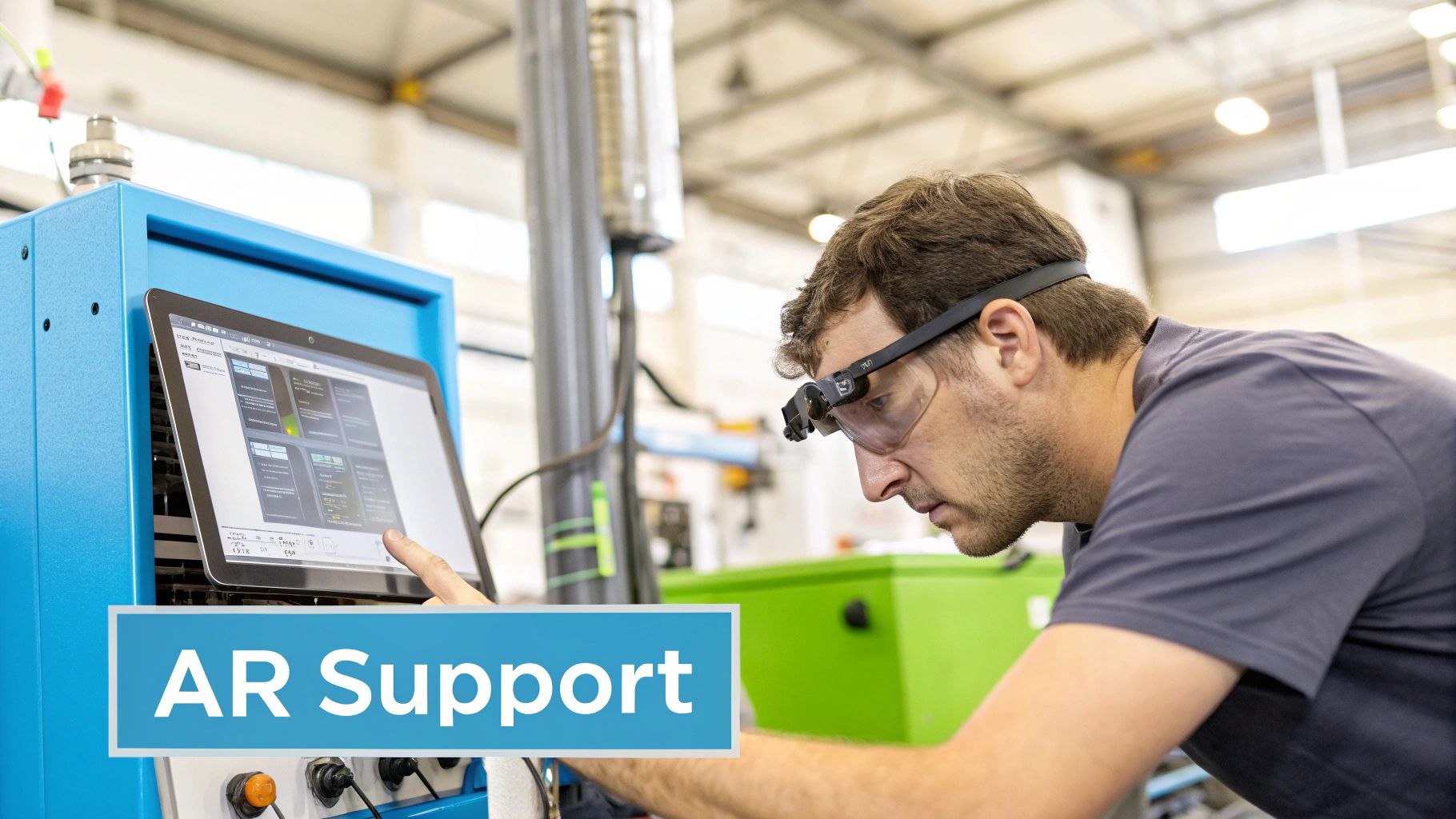

This “see-what-I-see” capability is the foundation of AR support. The remote expert isn't just listening to a second-hand description; they are virtually there, able to diagnose the problem with full visual context.
Driving First-Time Fix Rates with Digital Overlays
The real power of AR support emerges when you start overlaying digital information directly onto the real-world equipment. The remote expert can guide the local technician with incredible clarity, ensuring the right steps are taken in the right order.
This interactive guidance isn't just talk. It can include:
- Live Annotations: The expert can draw circles, arrows, and instructions that "stick" to specific components in the technician's view, eliminating any ambiguity.
- Document Sharing: A wiring diagram or step-by-step repair guide can be pulled up and displayed right in the technician’s field of vision.
- 3D Model Overlays: For complex repairs, a 3D model of a part can be superimposed over the actual equipment, showing exactly how it should be oriented or installed.
This level of precision slashes the chance of human error. The on-site tech is no longer working from memory or trying to interpret vague verbal directions. They have a clear, visual guide showing them exactly what to do, which is why companies using AR see a huge jump in first-time fix rates.
By bridging the gap between on-site personnel and off-site expertise, AR support makes your entire workforce more capable. It effectively multiplies the reach of your most skilled engineers, allowing them to troubleshoot issues at multiple facilities in a single day without ever leaving their office.
The Measurable Impact on Your Bottom Line
Implementing an AR support solution delivers immediate and measurable results. The efficiency gains go far beyond just fixing machines faster; they create a more resilient, cost-effective operation. If you want to get into the details of the technology, our guide on augmented reality remote assistance is a great place to start.
The financial and operational benefits are clear. Businesses that adopt this technology can significantly reduce service times, getting critical equipment back online in a fraction of the time. Better yet, by eliminating the need for specialists to travel to a site, companies can slash expert travel costs substantially. That's not just money saved on flights and hotels—it makes your best talent more available to solve more problems. It’s a powerful way to make your automation investment more robust and profitable.
Building Your Automation Implementation Roadmap
Embarking on a manufacturing process automation project without a clear plan is a recipe for failure. A strategic implementation roadmap is essential for navigating the complexities, avoiding common pitfalls, and ensuring your investment pays off. It breaks the process down into manageable phases, guiding you from the initial concept stage to a fully scaled, successful transformation.
A solid roadmap brings clarity, builds momentum, and keeps everyone—from the C-suite to the shop floor—aligned. It turns a massive, intimidating project into a series of achievable wins.
Phase 1: Assessment and Goal Setting
First, you need a crystal-clear picture of your current operations. Before you can automate anything, you must pinpoint the specific pain points and opportunities where automation will deliver the biggest impact. This means taking a deep dive into your existing workflows to find bottlenecks, repetitive tasks, and areas prone to errors or safety risks.
Once you know where the problems are, you can define what success looks like. It’s critical to set concrete, measurable Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) from the start.
Your goals can't be ambiguous. Move beyond vague ambitions like "improve efficiency." Get specific. Aim for something like, "increase production throughput by 15% within 12 months" or "cut defect rates on Line B by 20%."
These hard numbers become your north star for the entire project. They’ll help you justify the investment and, later on, prove your return.
Phase 2: Solution Design and Pilot Project
With your goals locked in, it’s time to start designing the right solution. This is where you’ll evaluate different technologies and select the ones that best fit your unique challenges. It's also the ideal time to identify potential partners who have the expertise to help you design and integrate the system smoothly.
A key best practice is to start small. A pilot project is a limited-scale trial focused on a single, high-impact area. This approach is smart for several reasons:
- Prove Value: You can demonstrate the real-world benefits of automation with a tangible, low-risk win.
- Learn and Adapt: It’s a chance to work out any issues with the technology and your process on a small, manageable scale.
- Build Momentum: A successful pilot builds confidence and gets everyone, from leadership to the frontline team, excited about a broader rollout.
Choosing the right pilot is key—it needs to be complex enough to be meaningful but simple enough to have a high probability of success.
Phase 3: Scaling and Change Management
After a successful pilot, it’s time to scale the solution across other parts of your operation. You’ll take the lessons learned from the pilot and apply them to a broader implementation plan. A phased rollout almost always works better than a "big bang" approach, as it gives your team time to adapt.
This brings us to the most critical—and most often overlooked—part of the process: change management. Introducing automation fundamentally changes how people do their jobs. You must be proactive with communication, develop clear training programs, and involve your workforce in the process from the start. Preparing your team for their new roles, which will focus more on managing and optimizing automated systems, is the secret to making the transformation stick for the long haul.
Got Questions About Automation? We've Got Answers.
Exploring the world of manufacturing process automation is bound to bring up some questions. That’s perfectly normal. Getting straight answers to those practical concerns is the best way to move forward, build a solid strategy, and get everyone on board.
Let's tackle some of the most common questions we hear from leaders who are considering automation.
"Where on Earth Do We Start?"
The best place to start is with your biggest operational headache. Take a hard look at your production line and find the most glaring bottlenecks, the most repetitive manual tasks, or the stations with the highest error rates. These are your prime opportunities—the spots where automation will deliver the biggest and fastest return.
Don't try to overhaul everything at once. Instead, pick one well-defined pilot project. This lets you prove the concept, learn invaluable lessons on a smaller scale, and build genuine enthusiasm from your team and leadership for a wider rollout.
"Will Robots Take Everyone's Jobs?"
This is a common concern, but the reality is much more nuanced. Automation isn’t about replacing people; it’s about elevating their roles. Automated systems are perfect for handling the tedious, physically draining, or hazardous tasks that are often inefficient and unsafe for humans.
This frees up your skilled employees to focus on work that requires human intellect—things like complex problem-solving, nuanced quality control, and optimizing the entire system.
The most successful automation projects treat technology as a tool to empower people, not replace them. When you invest in upskilling and modern training—especially with tools like AR and VR—you help your team transition smoothly into more strategic and engaging roles. Your entire operation becomes more valuable.
"How Do We Actually Measure the ROI?"
Measuring the return on an automation project is about tracking the right metrics before and after implementation. This isn't guesswork; it's a data-driven approach that paints a clear, undeniable picture of the project's real-world impact.
Here are the core metrics you should be watching:
- Increased Throughput: How many more units are you producing per hour or per shift? This is your raw productivity gain.
- Reduced Defect Rates: What percentage of products are failing QC? This shows improvements in precision and consistency.
- Lower Operational Costs: Track the savings from reduced labor hours on specific tasks, less material waste, and lower energy consumption.
- Improved Worker Safety: Are there fewer workplace incidents or injuries in the automated areas?
- Decreased Machine Downtime: How much more uptime are you getting from your critical equipment? More uptime equals more output.
Ready to see how immersive AR and VR solutions can accelerate your automation strategy and empower your workforce? The team at AIDAR Solutions can build a tailored plan to help you close the skills gap and transform your maintenance workflows. Learn more about our solutions.


