Augmented Reality in Automotive Driving’s Future
Imagine your car's windshield doing more than just keeping the rain out. Picture it transforming into an intelligent, active display that helps you navigate and stay safe. That's the reality of augmented reality in automotive—a technology that merges digital information, like navigation arrows and safety alerts, directly onto your view of the road.
This technology is designed to make driving safer, simpler, and far more intuitive.
What Is Augmented Reality in Automotive
At its core, automotive AR is all about overlaying computer-generated information onto the real world you see through your windshield.
A traditional GPS on a dashboard requires you to look down, process the information, and then apply it to the road ahead. An AR system, on the other hand, is like having a guide right there with you, projecting directions and highlighting potential hazards directly onto the road. The goal is to make the experience feel completely natural.
This is a practical evolution in how we interact with our cars. The goal is to provide critical data without requiring drivers to take their eyes off the road. By projecting information where it’s most useful—right in your line of sight—AR systems reduce distraction and can significantly improve reaction time.
Core Components of Automotive AR
A combination of key technologies work in sync to enable AR experiences.
- Sensors and Cameras: These are the car's "eyes." They constantly gather data on speed, position, and surrounding objects, from other cars to pedestrians.
- Processing Unit: This is the brain. It takes all that sensor data and, in a split second, determines what information you need to see.
- Display Technology: This is usually a Head-Up Display (HUD). It's the projector that beams the graphics onto the windshield, making them appear as part of the world outside.
This level of integration is becoming a major focus for car manufacturers. The global augmented reality automotive market is on track to hit USD 6.79 billion by 2025, growing at a rate of about 17.6% annually. This growth is fueled by AR being paired with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). You can dive deeper into the numbers in this detailed report on the automotive AR market.
Augmented reality transforms passive vehicle data into active, intuitive visual cues. Instead of just knowing your speed, you see a visual warning if you exceed the limit. Instead of glancing at a map, you see a glowing arrow on the exact lane you need to be in.
This shift is more than just a feature; it's a fundamental change in vehicle design and the driving experience. AR doesn't just add another screen. By providing information in context, it creates a more connected and aware driving environment. To get a better sense of this shift, you can learn more about how augmented reality is changing the automotive industry. This technology is redefining what we expect from our cars.
How AR Improves the Entire Automotive Lifecycle
Augmented reality’s impact on the automotive world extends beyond in-car displays. It provides value at every stage of a vehicle’s life, from the first digital sketch to the last service check. AR is becoming a core technology that helps build better, safer cars more efficiently than ever before, fundamentally changing how professionals design, build, and maintain them.
This process starts in the design studio. Traditionally, building a physical prototype was a slow and expensive affair. AR changes that. Now, designers and engineers can wear a headset and see a full-scale 3D model of a vehicle in the room with them. They can walk around the virtual car, open the doors, and sit inside to get a true feel for the ergonomics and visibility.
Interacting with a "digital twin" of the car this way is a massive accelerator. Engineers can swap out components, test different material finishes, or reconfigure the dashboard layout with a few hand gestures, seeing the changes in real-time. This rapid, iterative loop nearly eliminates the need for expensive physical prototypes, which shrinks development timelines and gives designers more room to innovate.
Streamlining Manufacturing and Assembly
Once the design is finalized, AR moves to the factory floor, where precision is paramount. A modern assembly line is complex, with thousands of parts and hundreds of precise steps for a single vehicle. AR acts as a real-time guide for workers.
Technicians wearing AR glasses can see step-by-step instructions, diagrams, and critical specs overlaid directly onto the part they’re working on. For instance, an AR system can highlight the exact bolt to tighten next and then visually confirm when the correct amount of torque has been applied. It's like having an expert looking over your shoulder for every task.
This digital assistance brings significant advantages:
- Error Reduction: Visual cues ensure the right part is used in the right place every time. This drastically cuts down on human error, with some studies showing AR can boost quality control by up to 90% in industrial settings.
- Faster Training: New employees can get up to speed in a fraction of the time. Instead of studying dense manuals, they learn by doing, with AR guiding them through each step.
- Increased Efficiency: Workers don't need to stop to check a manual or a computer terminal. All the information they need is hands-free and in their line of sight, which can increase productivity by over 30%.
The image below gives a glimpse of how AR navigation is a common application of this technology, but the core principle of clear, contextual guidance is the same one transforming the factory floor.
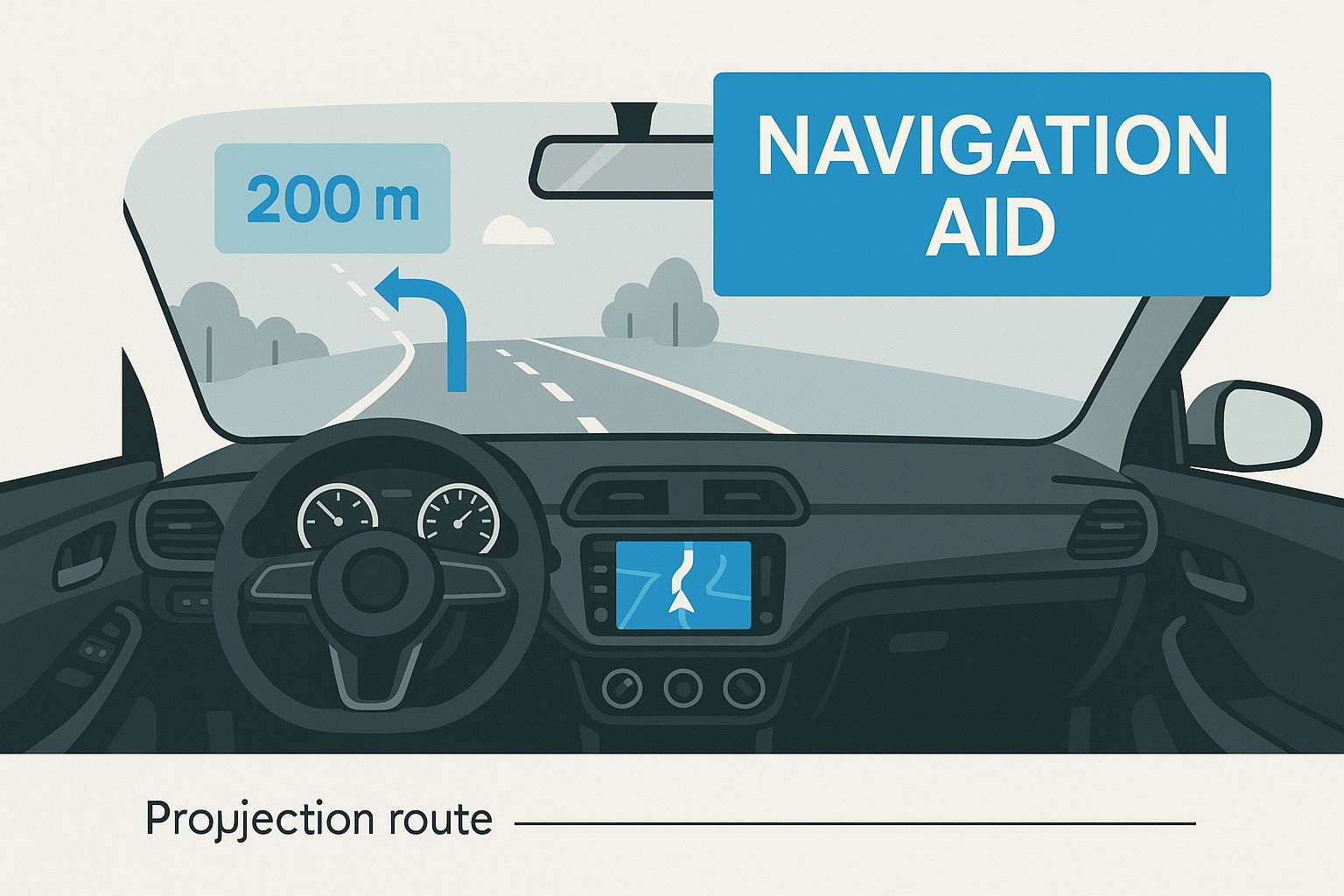
This intuitive, visual support is what makes AR so powerful, whether it's helping a driver navigate a busy street or a technician assemble a complex engine.
Transforming Vehicle Service and Maintenance
AR's role continues into the service bay. Today’s cars are complex machines, and diagnosing a problem can be challenging. AR gives mechanics a form of digital X-ray vision to cut through the complexity.
By pointing a tablet or wearing smart glasses at a vehicle, a technician can "see through" body panels to the components underneath. The system can overlay wiring diagrams, identify specific parts, or highlight the source of a fault code.
This is a significant advancement for diagnostics and repair. A mechanic can pull up a vehicle's full service history and follow guided, step-by-step repair instructions projected right onto the engine bay. If they encounter a difficult problem, they can even use the AR headset to share their live point-of-view with a remote expert for instant help.
This approach slashes diagnostic time, improves first-time fix rates, and ensures every repair is done to manufacturer specifications. By making complex information simple and visual, AR is making vehicle maintenance faster and more accurate.
AR's versatility allows it to add value across the entire automotive journey. Here’s a quick breakdown of where it fits in.
AR Applications Across the Automotive Value Chain
This table illustrates the diverse use cases of augmented reality at different stages of the automotive industry, from conception to maintenance.
| Lifecycle Stage | AR Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Design & Prototyping | Virtual 3D vehicle modeling and review. | Reduces need for physical prototypes, accelerates iteration, and improves collaborative design. |
| Manufacturing | Step-by-step assembly guidance and quality control overlays. | Minimizes errors, speeds up production and training, and increases overall efficiency. |
| Sales & Marketing | Virtual showrooms and interactive vehicle configurators. | Creates engaging, personalized customer experiences and showcases features effectively. |
| In-Car Experience | Heads-up displays (HUDs) with navigation and safety alerts. | Enhances driver awareness and safety by keeping eyes on the road. |
| Service & Maintenance | "X-ray vision" diagnostics and remote expert assistance. | Drastically reduces repair times, improves first-time fix rates, and boosts accuracy. |
As you can see, AR is a foundational technology that enhances precision, speed, and understanding at every touchpoint.
Making Driving Safer with AR Head-Up Displays
Beyond the factory and design studio, augmented reality is making its most direct impact in the driver's seat. Here, the technology turns the windshield into an active safety feature with advanced AR Head-Up Displays (HUDs). These systems are all about creating a safer, less distracting cockpit by blending critical information right into your view of the road.
An AR HUD is much more than a simple data projector. It acts as a smart co-pilot. It takes data from the car’s sensors—GPS, cameras, radar—and projects intuitive visual cues directly onto the windshield. The information looks like it's part of the real world, exactly where your focus needs to be.
The biggest benefit here is a massive reduction in cognitive load. Instead of glancing down at the dashboard or a separate screen, your eyes stay on the road. Information appears exactly when and where it’s most relevant, which can make a huge difference in awareness and reaction time.

From Data Projection to Intuitive Guidance
Traditional HUDs are fairly basic; they show static info like your speed or a simple arrow for the next turn. AR HUDs are far more advanced. They make the data dynamic and interactive with the environment around you. It’s the difference between being told what to do and being shown what to do.
This contextual guidance is powered by the vehicle’s Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS). The AR system pulls together data from all those sensors to build a live digital model of your surroundings. It then uses that model to place graphics in a way that feels perfectly anchored to reality.
The whole point of an AR HUD is to translate complex vehicle data into simple, unmistakable visual signals. It helps drivers understand and react to situations faster, effectively turning the windshield into an intelligent co-pilot.
This approach is a game-changer in high-stress situations. Whether you're navigating a confusing multi-lane highway or reacting to a sudden hazard, the AR display cuts through the noise and provides clear, unambiguous instructions.
Real-World Scenarios in an AR Cockpit
To fully appreciate the safety benefits, let's look at a few practical examples of how augmented reality in automotive HUDs work on the road:
-
Turn-by-Turn Navigation: When approaching a complex highway interchange, instead of looking at a map icon, the AR HUD projects a large, glowing arrow that appears "painted" onto the exact lane you need to be in. The arrow moves and scales as you get closer, eliminating confusion.
-
Hazard Identification: If the car’s sensors spot a pedestrian about to step into the road, the AR HUD can instantly draw a bright, highlighted box around them, grabbing your attention and alerting you to the danger before you might have noticed it yourself.
-
Lane Departure Warnings: If you start drifting out of your lane without signaling, the system can project a vibrant line along the lane marking you're about to cross, giving you an instant visual cue to correct your steering.
-
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) Visualization: When ACC is active, the AR display can highlight the car you're following with a colored marker. It’s a simple visual confirmation that the system has locked onto the right vehicle, building trust in the technology.
This blend of real-time alerts and navigational aids is what’s driving market growth. By 2024, various market analyses predict the automotive AR market will be valued somewhere between USD 1.42 billion and USD 6.10 billion. This growth is all about rising consumer demand for smarter safety features, and AR is perfectly positioned to deliver by making sense of sensor data and flagging threats for the driver. You can find more details in this report on the growing automotive AR market trends.
Ultimately, AR HUDs represent a fundamental shift in how people and cars interact. By putting the right information in the right place at the right time, they make driving not just more convenient, but demonstrably safer.
Real-World Examples of AR in Modern Cars
Augmented reality in the automotive world is no longer just a concept for car shows. It is already integrated into many of today's cars. Automakers are using it to solve real, everyday driving challenges, proving its practical value.
The most common application of AR is in next-generation navigation systems. Instead of a 2D map, these systems use a live feed from a front-facing camera and overlay animated arrows, lane guidance, and street names right onto the video on your infotainment screen.
This creates a perfect link between the digital directions and the road in front of you. When approaching a confusing city intersection, the system shows an arrow that looks like it's floating over the exact lane you need to be in, eliminating guesswork.

Making Difficult Maneuvers Simple
Parking in tight spaces is another area where AR is a game-changer. Many new cars feature AR-powered parking assistants that do more than just show a camera feed. These systems project the car's turning radius and planned path onto the live video.
As you turn the wheel, you see a dynamic overlay showing precisely where your tires will go. This visual guidance makes parallel parking or backing into a cramped garage spot incredibly easy and far less stressful. It turns a guessing game into a clear, predictable maneuver.
This is a perfect example of AR's core strength: it takes complex vehicle data—like your steering angle—and translates it into simple, intuitive visuals that the driver can act on instantly.
The AR-Enabled Owner's Manual
The usefulness of AR doesn't stop when you turn off the engine. It's also changing how we handle basic vehicle maintenance, thanks to interactive, AR-enabled owner's manuals. Now, you can just use your phone.
Simply point your phone's camera at something under the hood, and the AR app can identify it and overlay useful information right on your screen. It could be as simple as labeling a part or as helpful as showing you a step-by-step guide for a basic task.
This digital-first approach makes owning a car feel more accessible, empowering drivers to understand the machine they're operating. Some of the most useful features include:
- Component Identification: Point the camera at the engine, and labels can pop up for the oil dipstick, windshield washer fluid, or brake fluid reservoir, taking the intimidation out of looking under the hood.
- Interactive How-To Guides: The app can show an animated overlay demonstrating exactly how to check your oil or replace an air filter, guiding you through the process visually.
- Warning Light Explanations: When a warning light appears on your dash, the AR app can identify it and provide a plain-English explanation of what's wrong and what you should do next.
These real-world examples make it clear that augmented reality is already woven into the fabric of the modern driving experience. From navigating busy streets to topping off your washer fluid, AR is delivering practical solutions that make driving and owning a car safer, easier, and more intuitive.
How to Implement an Automotive AR Strategy
Integrating augmented reality into automotive operations requires a solid plan. A clear roadmap is what separates a gimmick from a real competitive advantage. The first step starts with understanding specific business challenges.
You need to pinpoint where AR can make the biggest impact by identifying operational pain points. Are assembly line error rates too high? Is training new technicians taking too long? These are the kinds of problems AR is designed to solve.
For example, using AR for manufacturing training can directly address skill gaps and get new hires productive in record time. We've explored this in depth, looking at how the automotive industry trains employees in virtual reality to see just how powerful it can be. Focusing on these key areas ensures your investment is effective from day one.
Building Your Technology Stack
Once you know what problems you want to solve, it’s time to choose the right hardware and software. This decision must link directly to your specific use case.
- Hardware Selection: For hands-on jobs like maintenance or assembly, smart glasses are an ideal choice, as they keep a technician's hands free. For improving the in-car experience, embedded projectors for AR Head-Up Displays (HUDs) are required.
- Software Development: The choice between building a custom application or working with a specialized provider depends on your in-house talent and project complexity. A custom build offers a perfect fit for your workflows, while an existing platform can get you operational much faster.
A crucial piece of the software puzzle is data integration. Your AR system needs to communicate with other platforms—like Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) or inventory management software—to pull in real-time, relevant information.
The real value is created when you design a user interface (UI) that feels natural. The technology should be an assistant, not a distraction, whether for a mechanic in the garage or a driver on the road.
Modern AR systems deliver a rich experience by combining audio, visual, and even haptic feedback. This allows them to provide real-time navigation, vehicle diagnostics, and collision warnings without distracting the driver. Windshield AR HUDs that overlay critical info in the driver’s line of sight are central to this. As computer vision and IoT improve, the integration of AR and ADAS will only get stronger, boosting situational awareness and making roads safer.
A Phased Rollout for Sustainable Success
A company-wide AR deployment from the start is a risky move. A smarter approach is a phased rollout, beginning with a focused pilot program. This lets you test the technology in a controlled environment, gather user feedback, and measure your ROI with hard data.
Remember, any AR solution that relies on AI to process the world is only as good as the data it's trained on. This is where high-quality data annotation becomes essential. It’s what teaches the AI models to correctly recognize objects and overlay information accurately.
Design your pilot program to test assumptions and refine the user experience. By starting small, you can fix problems, prove the value to key stakeholders, and build the confidence needed for a successful, large-scale rollout.
Measuring the ROI of Your AR Investment
Adopting augmented reality is a significant step, and it's important to understand the financial impact. To measure ROI, you have to look beyond initial setup costs and consider both direct savings and long-term value.
It helps to break the benefits into two categories. The first is tangible ROI—the hard-number savings that you can track and that directly impact your operational budget.
The second is intangible ROI. This is more difficult to measure but is critical for building a competitive brand. It represents the value gained from improving market perception and customer satisfaction.
Calculating Tangible Financial Gains
Tangible ROI is the most direct way to prove the worth of augmented reality in automotive projects. These are the measurable wins in efficiency and cost-cutting. For instance, putting AR guides on the manufacturing line can seriously cut down on assembly errors, which means less wasted material and fewer expensive reworks.
Here are a few key tangible metrics to track:
- Reduced Repair Times: When technicians use AR for diagnostics and maintenance, they can slash the time it takes to service a vehicle. Some solutions have been shown to speed up diagnostics and repairs by 30%.
- Decreased Prototyping Costs: During the design phase, using AR to visualize and tweak digital twins nearly eliminates the need for expensive physical prototypes, saving time and money.
- Lower Training Expenses: Immersive AR training gets new technicians up to speed much faster and more effectively than traditional methods, cutting costs associated with long training programs.
Metrics like these provide a clear financial case for implementing AR. If your business is focused on vehicle service, taking a closer look at specific applications for augmented reality for maintenance can uncover even more ways to save money directly.
Understanding Intangible Value
Intangible benefits are about building a long-term strategic edge. You might not be able to assign an exact dollar figure to them immediately, but their impact on profitability and market standing is undeniable. This is the future-proofing side of your AR investment.
Intangible ROI is about securing your market position. It’s the difference between being a follower and a leader in an industry where technology defines the customer experience and operational excellence.
Consider the powerful signal AR sends about your brand. A company using AR in its service bays or building it into its cars is immediately seen as a technology leader. That alone can elevate your brand and influence purchasing decisions. Other intangible perks include stronger customer loyalty from faster, more accurate service and the potential for better vehicle safety ratings thanks to AR-powered driver-assistance features. Over time, these factors build a much stronger, more valuable brand.
Common Questions About Automotive AR
As augmented reality starts showing up in more vehicles, questions naturally arise. Let's tackle some of the most common ones to get a clearer picture of how this technology works for drivers, mechanics, and carmakers.
What’s the Difference Between AR and VR in Cars?
The easiest way to think about it is how each technology interacts with the world around you.
Augmented Reality (AR) adds a digital layer on top of what you're already seeing. Think of navigation arrows that appear to float over the actual road ahead of you on your windshield. It’s all about enhancing reality, not replacing it.
Virtual Reality (VR), on the other hand, immerses you in a totally digital, computer-generated world. It completely blocks out your physical surroundings. In the auto industry, VR is a powerful tool for things like designing a car's interior in a virtual studio or running training simulations in a controlled, synthetic environment.
AR is a digital overlay on the real world, while VR builds a brand-new digital world from scratch. When you're driving or fixing a car, enhancing reality is almost always more practical than shutting it out.
Is an AR Display Distracting for the Driver?
This is a major concern, as safety must come first. It might sound counterintuitive, but AR displays are actually designed to reduce distraction by keeping the driver’s eyes on the road.
Critical information is carefully placed in the driver's natural line of sight. The visuals are often semi-transparent, so they inform you without blocking your view of a pedestrian or another car.
Automakers put these systems through extensive testing to ensure the graphics are genuinely helpful, not just more visual noise. The goal is to lower the mental effort needed to process key information, like your speed or the next turn.
This same principle of clear, simple communication makes AR an incredible tool for technicians, too, radically improving their expertise and efficiency. You can see just how powerful it is for skill-building in our guide to augmented reality for training. Ultimately, when implemented correctly, AR is a safety feature, not a distraction.
At AIDAR Solutions, we're experts in building AR and VR applications that make work safer and more efficient. Our solutions are designed from the ground up to improve training and operational workflows, delivering a clear and rapid return on your investment. Discover how our expertise can support your business goals.

