A Practical Guide to Augmented Reality Training
Traditional training methods often create a disconnect from real-world application. Employees learn in a classroom or from a manual, and are then expected to apply that theoretical knowledge on the job, recalling diagrams and abstract steps under pressure. Augmented reality training fundamentally changes this dynamic.
It works by overlaying digital instructions, 3D models, and real-time guidance directly onto an employee's view of their actual workspace. This technology provides the equivalent of an expert technician standing beside every new hire, pointing out the exact wire to connect or the precise component to inspect. Using common devices like smartphones or specialized smart glasses, it effectively bridges the gap between knowing what to do and actually doing it.
What Is Augmented Reality Training?
At its core, augmented reality training moves learning out of the static manual and directly into the physical world. Instead of forcing employees to memorize procedures out of context, they learn by doing, with digital cues layered right on top of the equipment they're working on.
This creates a powerful, intuitive link between understanding a task and performing it correctly. It's a practical approach that transforms how skills are developed, which is the core principle behind effective AR for training.
Bridging Theory and Practice
The primary value of AR is how it closes the gap between the training room and the job site. This disconnect is where mistakes happen and productivity stalls. By merging the learning and working environments, the benefits become immediately clear:
- Faster Skill Development: With interactive, step-by-step guidance, employees can tackle complex jobs much faster and with greater confidence.
- Reduced Mental Strain: Trainees no longer need to recall complex procedures from memory. The instructions appear exactly where and when they're needed, allowing them to focus completely on the task at hand.
- A Safer Way to Learn: AR can instantly highlight hazardous areas, display safety warnings, and ensure every step of a critical procedure is followed precisely, drastically reducing accidents.
AR creates a safe, practical training ground where employees build muscle memory and competence without the high-stakes risks of real-world mistakes.
When you look at the data, the advantages become even more stark.
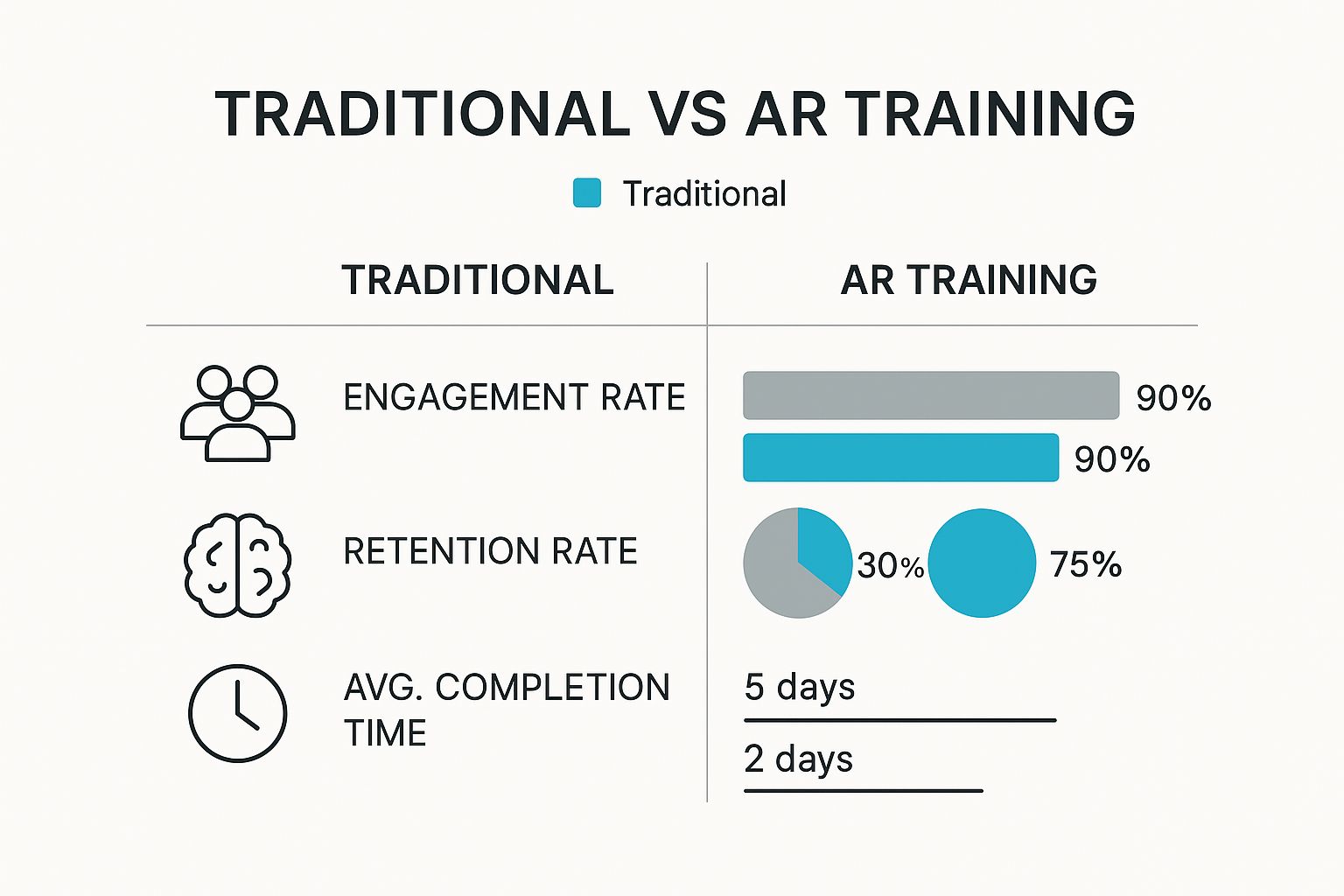
As the numbers show, AR training isn't just a minor improvement; it's a significant leap forward in engagement, knowledge retention, and the speed at which people master new skills.
The market is certainly taking notice. As of 2024, the global augmented reality training and education market hit a value of around $31.26 billion. But that's just the start. It’s projected to skyrocket to $51.34 billion by 2025, a clear sign of just how influential this technology is becoming.
Comparing Training Methods Side-by-Side
To truly grasp the shift AR represents, it helps to compare it directly with traditional methods. The differences in engagement, retention, and real-world applicability are significant.
| Feature | Traditional Training | Augmented Reality Training |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Environment | Classroom or separate training area, away from the job. | Directly on the job site, interacting with real equipment. |
| Information Delivery | Static manuals, presentations, or video demonstrations. | Interactive, real-time 3D overlays and step-by-step guides. |
| Knowledge Retention | Relies on memorization; retention rates can be as low as 10%. | "Learn-by-doing" approach boosts retention to over 75%. |
| Error Correction | Feedback is often delayed or requires an instructor's presence. | Instant, on-screen feedback prevents mistakes as they happen. |
| Scalability | Limited by instructor availability and physical space. | Infinitely scalable; deployable to any employee, anywhere. |
| Safety | Simulates hazards but can’t fully replicate real-world risks. | Can highlight live dangers and guide safe procedures in real-time. |
Ultimately, while traditional methods have their place, they cannot match the hands-on, contextual, and deeply engaging nature of AR-based learning. It's a fundamental move from passive observation to active participation.
The Real-World Business Wins of AR in Workforce Development
Integrating augmented reality into a training program is not just about modernization; it's about generating tangible business results that impact the bottom line. By creating a 'learn-by-doing' environment that is both safe and realistic, AR builds a workforce that's more confident, capable, and productive.
This value is delivered through four key pillars: improved safety, accelerated proficiency, reduced errors, and boosted efficiency. Each of these benefits stems from AR’s unique ability to put critical information exactly where employees need it—right in their line of sight as they perform a task.

A Major Leap Forward in Workplace Safety
In high-stakes industries, safety is paramount. AR training acts as a powerful preventative measure, mitigating the risk of accidents before they have a chance to occur.
Consider a new technician faced with complex, intimidating machinery. With an AR overlay, high-voltage areas can be instantly highlighted, dangerously hot components can be flagged, and incorrect procedural steps can be caught in real time. This functions like a digital safety supervisor, ensuring protocols are followed precisely. This is absolutely critical in industries like manufacturing or utilities, where a single mistake can lead to disaster.
By allowing employees to practice hazardous tasks in a controlled virtual space, they build crucial muscle memory and situational awareness without exposure to real danger.
Getting Employees Up to Speed, Faster
The traditional learning curve is often slow and expensive. AR radically shortens the time it takes for an employee to become fully competent and productive. Instead of relying on dense manuals or shadowing a senior colleague, a new hire can begin tackling complex jobs from day one with guided assistance.
For example, a surgeon-in-training can practice an intricate procedure by following a 3D anatomical model overlaid on a manikin. The AR system guides their every move, helping them build precision and confidence long before stepping into a live operating room.
This hands-on, guided approach lets employees master skills through repetition in realistic scenarios. It enables organizations to turn novices into experts at an accelerated pace.
This acceleration is a cornerstone of effective workforce development strategies, ensuring your teams are skilled up and ready to meet business demands.
Slashing Costly Human Errors
Mistakes in assembly, maintenance, or repair lead to wasted materials, product defects, and expensive rework. Augmented reality addresses this problem by delivering clear, step-by-step visual instructions.
Imagine a worker on an assembly line. AR glasses can project a visual checklist and highlight the exact components to use for each step, ensuring 100% accuracy. If they select the wrong part, the system can display an immediate alert, stopping the error before it progresses down the line.
The impact on error reduction is significant:
- Fewer Defects: Guided instructions ensure every product is built to exact specifications.
- Less Material Waste: Preventing mistakes saves substantial costs on discarded parts and materials.
- Better Quality Control: AR functions as a real-time quality check, maintaining high standards from start to finish.
Unlocking New Levels of Operational Efficiency
Ultimately, a safer, faster, and more accurate workforce is a more efficient one. AR streamlines workflows by reducing the time people spend searching for information or waiting for expert assistance.
A field service technician can use AR to see repair schematics overlaid directly onto the equipment they’re fixing. This eliminates the need to consult a laptop or a manual. Their hands remain free, and their focus stays on the job. This leads to quicker diagnostics and higher first-time fix rates—a direct benefit for customer satisfaction and operational throughput. By giving every employee expert-level guidance on demand, businesses can unlock new levels of productivity.
AR Training Applications Across Industries
The practical value of augmented reality training is best demonstrated by its real-world applications. This is not a one-size-fits-all technology; it is a flexible tool that adapts to the unique challenges of different industries, from the factory floor to the operating room.
Examining these practical use cases is the best way to envision how AR could be implemented in your own operations.

This trend is part of a broader shift toward immersive learning. Virtual reality (VR) training, a related technology, is also attracting massive investment. The global VR education market reached $4.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to $28.7 billion by 2030.
With a significant 40.3% increase in demand for AR and VR training technology in 2022 alone, it is clear that companies are recognizing the power of hands-on, digital development.
Manufacturing and Assembly
In manufacturing, precision is essential. Errors lead to costly rework and delays. AR training is a transformative solution in this area, guiding workers step-by-step through even the most complex assembly tasks.
Imagine a new hire assembling a sophisticated piece of equipment. Through AR glasses, they see digital instructions superimposed over the real components. An arrow points to the exact screw to tighten, a pop-up shows the correct torque setting, and the next part in the sequence is highlighted.
A dense, confusing manual becomes a live, interactive guide. This virtually eliminates common mistakes and ensures every product is built to specification.
Healthcare and Surgical Training
The stakes are highest in healthcare, where there is no room for error and training must be impeccable. AR offers a safe, repeatable, and highly realistic environment for medical professionals to practice and refine their skills.
Surgeons can rehearse complex procedures on a 3D anatomical model digitally overlaid onto a physical manikin, building the muscle memory and confidence required without ever putting a patient at risk.
This technology is critical for:
- Visualizing Anatomy: Trainees can interact with a 3D model of the human body, exploring organs and systems from any angle to better understand their connections.
- Procedural Guidance: During simulations, AR can provide real-time prompts and instructions, guiding a surgeon's hands through the correct steps.
- Remote Mentorship: An expert surgeon located miles away can see exactly what a trainee sees and provide live guidance as if they were in the same room.
Logistics and Warehouse Operations
Logistics is a discipline of speed and accuracy. AR-powered smart glasses are transforming warehouse operations by making the picking and packing process faster and more intuitive.
A worker wearing AR glasses receives visual cues in their line of sight, guiding them along the most efficient path to the next item on their list. Upon arrival, the correct bin is highlighted digitally, and the quantity to pick is displayed directly in their view.
This hands-free approach has been proven to dramatically boost picking speeds and reduce error rates, resulting in more orders being processed accurately and efficiently. To see more examples of this in action, check out our guide on augmented reality industrial applications.
Field Services and Remote Assistance
For a field technician, the primary goal is a first-time fix. Requesting backup or scheduling a second visit costs time and money. AR connects on-site technicians with senior experts for instant help, reducing the need for repeat visits.
Imagine a junior technician encountering a machine they have never serviced before. They can put on their AR headset and share their point-of-view with a veteran engineer at the main office. The expert can then draw on the technician's live video feed, circling a faulty component or displaying a schematic directly on the equipment.
This “see-what-I-see” support provides every technician with access to the collective knowledge of the entire company, right when they need it most.
How to Implement Your AR Training Program
Transitioning from the concept of AR training to a functional program that your team uses effectively requires a strategic plan. It is a deliberate process that starts with identifying where AR will make the most significant impact.
Before considering hardware or software, you must identify the most pressing training gaps in your organization. Where do new hires struggle? What specific tasks lead to the most mistakes or safety issues? Pinpointing a high-impact use case from the start sets you up to solve a real, measurable problem.
Define Clear Learning Objectives
Once you have a target, you need to define what success looks like. Vague goals like "improve training" are insufficient. You must set specific, measurable objectives for your augmented reality training program.
Think in terms of tangible results. For example:
- Reduce the assembly time for Product X by 15%.
- Decrease material waste caused by user error by 20% in the first quarter.
- Achieve a 95% first-time pass rate on a critical safety procedure.
Metrics like these serve as your guiding principles. They direct the creation of your AR content and simplify the process of proving the ROI of your investment later on.
Choose the Right Hardware and Software
With clear goals established, it's time to select your tools. This decision should be based on the real-world demands of the job you are trying to improve. It is not always necessary to procure the most expensive, high-tech equipment to get started.
For many tasks, the devices your team already possesses are sufficiently powerful. Smartphones and tablets are a practical entry point into AR, making it fast and affordable to begin. However, for jobs that require hands-on work—such as complex repairs or detailed assembly—investing in AR smart glasses is the more effective choice.
The key is to match the hardware to the workflow. Forcing a tool that does not fit the task creates user frustration and hinders adoption of the new system.
Regarding software, there are two primary routes. You can partner with a development agency to build a custom solution tailored to your specific needs. If you have an in-house team, a good mobile app development guide can provide a solid starting point. The alternative is to use an off-the-shelf AR platform that allows your own experts to build and share training modules without writing any code.
Pilot, Gather Feedback, and Scale
Avoid rolling out a new program to the entire company at once. Start small. Run a controlled pilot program with a select group of trainees and instructors. This provides a safe environment to test everything—the content, the hardware, and the user experience—and gather honest feedback without high stakes.
Listen to that feedback and use it to refine the program before scaling up. This iterative approach ensures your full launch is smooth, effective, and built on a proven foundation. The market is ready for this kind of careful planning; valued at around $108 billion in 2024, the global AR market is expected to jump to $149.57 billion in 2025. This shows a healthy, maturing ecosystem of hardware and software ready to be implemented.
Measuring the ROI of Augmented Reality Training
Any new technology introduced into a business must demonstrate its value. This is especially true for an investment like augmented reality training. To build a compelling business case, you must look past the initial novelty and focus on measurable results. Calculating the return on investment (ROI) is not merely an accounting exercise; it is about showing how AR is a strategic financial decision that directly strengthens your bottom line.
The first step is to establish a clear baseline of your current performance. Before implementing AR, you need to have your existing metrics documented. How long does it take to onboard a new hire to full productivity? What are your current error rates on a specific assembly line? These numbers are your baseline, the "before" state you'll use for comparison.

Key Metrics for Direct Cost Savings
The most straightforward benefits to track are direct financial gains. These are the tangible savings that appear clearly on your budget, making them powerful evidence for your ROI calculation.
- Reduced Training Time: If traditional onboarding takes 40 hours, but AR training achieves proficiency in just 25, you have saved 15 hours of labor cost per person. Multiply that by the number of new employees you train to see how quickly those savings accumulate.
- Lower Error Rates: Every mistake has a cost—wasted materials, rework, lost time. By tracking the reduction in defect or scrap rates after implementing AR, you can assign a direct dollar value to the improvement in quality.
- Decreased Travel Costs: When you use AR for remote assistance, you eliminate the need to send an expert to a job site. A single avoided trip can save thousands in flights, hotels, and productivity, often paying for the technology investment almost instantly.
Quantifying Indirect Benefits
Not all benefits are immediately visible on a balance sheet. However, these indirect returns are critical to the long-term health and success of your business. They may be harder to quantify, but their financial impact over time can be substantial.
Attributing value to indirect benefits is a critical part of building a complete ROI picture. Improvements in safety, for example, lead to lower insurance premiums and fewer costs associated with workplace incidents.
Consider these powerful, though less obvious, returns:
- Improved Employee Safety: A reduction in safety incidents or near-misses is a significant metric. Fewer accidents mean less downtime, lower workers' compensation claims, and a safer, more confident workforce.
- Increased Employee Retention: High turnover is a significant hidden cost. If AR training leads to more engaged, capable employees who remain with the company longer, you save substantially on recruitment, hiring, and lost institutional knowledge.
- Higher First-Time Fix Rates: For any field service team, completing the job correctly on the first visit is a key efficiency metric. It boosts customer satisfaction and frees up technicians to handle more service calls.
By combining these direct savings and indirect gains, you can build a comprehensive and undeniable business case for AR. For a deeper dive into this process, our guide on how to measure training effectiveness offers valuable insights. This approach proves that augmented reality isn't just another operational tool; it’s a powerful engine for financial growth.
Got Questions About AR Training? We've Got Answers.
Adopting any new technology raises questions. When considering a significant operational shift like integrating augmented reality training, it is important to have a clear understanding of the implications.
Let's address the most common questions from decision-makers to provide clarity on the path forward.
What’s the Real Difference Between AR and VR Training?
This is a frequent and important question. The primary difference lies in how each technology interacts with your perception of reality.
Augmented Reality (AR) training keeps you grounded in your actual environment. It layers digital guides, 3D models, or instructions directly over the physical equipment you are viewing. It is analogous to an expert standing beside you, pointing out exactly which button to press or which part to fix on a real machine.
Virtual Reality (VR) training, in contrast, immerses you in a completely new, computer-generated world. It replaces your surroundings entirely. VR is the ideal solution when the real-life scenario is too dangerous, expensive, or impractical to replicate—such as for high-stakes safety drills or practicing a complex surgery without any risk.
Do I Need to Buy Expensive Headsets to Get Started?
No, this is a common misconception. While specialized hands-free smart glasses are excellent for complex, on-the-job tasks, they are not the only option.
In fact, some of the most effective AR training programs run on the hardware your team already uses daily: their smartphones and tablets.
Starting with a mobile-first approach is a smart, cost-effective way to pilot an AR program. You can prove its value with a small investment and then scale up to specialized hardware as your needs and the program itself grow.
This flexibility allows you to enter the space and demonstrate a solid ROI without budgeting for a massive upfront hardware purchase for every employee.
How Do We Actually Create the Content for AR Training?
Creating compelling AR content is more accessible than many people realize. There are several paths you can take, depending on your needs and in-house capabilities.
Here are the three main approaches:
- Use No-Code AR Platforms: Modern tools are designed for subject matter experts. These platforms allow your specialists to build and deploy training modules themselves, without requiring any coding knowledge.
- Bring in a Development Partner: For highly customized or complex workflows, you can collaborate with a specialized agency. They will build bespoke AR content that is perfectly matched to your operations.
- Grab Off-the-Shelf Solutions: For many common industrial machines and tasks, pre-built training modules are already available. This is often the fastest way to get up and running.
The right choice depends on your company's specific needs, your budget, and the technical comfort level of your team. By evaluating these factors, you can select a content strategy that begins delivering value immediately.
Ready to see how AR can reshape your workforce development? AIDAR Solutions provides immersive AR and VR applications that accelerate employee learning and streamline support workflows. Discover our tailored solutions and start building a more capable, efficient team today.


