A Guide to Augmented Reality Workflow Optimization
An augmented reality workflow is a system that layers digital information directly onto a physical environment, guiding users through tasks in real time. Instead of referencing paper manuals or switching between a screen and the task at hand, it delivers interactive, contextual instructions through devices like smart glasses or a tablet. This approach makes even the most complex processes more intuitive and efficient.
What Is An Augmented Reality Workflow?
Traditional methods of instruction can be compared to navigating a new city with a paper map. The information is available, but it requires the user to stop, find their current location, interpret the map, and then apply that information to the physical environment. This process is functional but slow and prone to error.
An augmented reality workflow, in contrast, functions like a live GPS that projects turn-by-turn directions directly onto the view of the road. It delivers the necessary information exactly when and where it is needed, blending seamlessly with the user's perception of reality. This is the core value of AR in an industrial setting: it transforms how frontline workers access and interact with critical data.

This approach empowers employees by converting complex, multi-step procedures into simple, guided experiences. A technician can view a 3D animation of a repair sequence overlaid on the actual machine they’re servicing, rather than interpreting a dense manual or waiting for remote expert assistance.
The Shift From Static To Dynamic Guidance
The key innovation is the transition from static, one-size-fits-all instructions to dynamic, context-aware support. An AR system can deliver information tailored to the specific equipment, the user's skill level, and the precise task being performed. This real-time guidance has a direct and measurable impact on operational outcomes.
To better understand this shift, let's compare the two approaches.
Traditional vs Augmented Reality Workflows
| Aspect | Traditional Workflow | Augmented Reality Workflow |
|---|---|---|
| Information Source | Paper manuals, PDFs, separate screens | Digital overlays on the real world |
| Guidance Style | Static, text-heavy, requires interpretation | Dynamic, visual, step-by-step |
| Cognitive Load | High (memory, interpretation, context-switching) | Low (information is contextual and immediate) |
| Error Rate | Prone to human error and misinterpretation | Significantly reduced through visual confirmation |
| Training Method | Classroom-based, shadowing senior staff | On-the-job, self-paced, guided training |
| Remote Support | Phone calls, video chats, travel required | "See-what-I-see" support with live annotations |
This comparison highlights the fundamental difference: AR closes the gap between knowing what to do and knowing how to do it, right at the point of action.
Implementing this approach yields immediate benefits:
- Improved Accuracy: Visual, step-by-step instructions dramatically reduce the likelihood of human error, ensuring tasks are completed correctly the first time.
- Increased Efficiency: Workers spend less time searching for information and more time performing the task, leading to faster completion times.
- Enhanced Safety: Critical warnings and hazard notifications can be displayed directly in a worker's line of sight, helping to prevent accidents.
- Accelerated Training: New hires can learn complex jobs much faster with immersive, on-the-job training modules that provide real-time guidance.
An augmented reality workflow closes the gap between the digital and physical worlds. It puts the right information in the right place at the right time, minimizing cognitive load and maximizing performance for your frontline teams.
Understanding The Broader Context
To fully appreciate AR’s impact, it helps to understand what workflow automation entails, as AR often applies digital automation principles to physical tasks. This is no longer a niche trend. By 2025, 75% of the global population is expected to be active AR users, primarily through mobile devices.
This large-scale adoption creates significant opportunities for businesses to reimagine their operations. As the general population becomes more familiar with AR technology, its application in specialized industrial settings becomes a logical and powerful progression. For a closer look at its practical uses, see our guide on the benefits of augmented reality for businesses.
The Core Components of an AR Workflow
A successful augmented reality workflow depends on three interconnected components working in concert: hardware, software, and data. Each element is critical; a deficiency in one can compromise the entire system. Understanding how these components integrate is the first step toward building an effective AR process. Let's examine each one.
Hardware: The Gateway to the Digital Overlay
Hardware serves as the physical interface between the user's real-world environment and the digital information overlay. It provides the sensory input and display capabilities necessary for an immersive experience. The choice of hardware directly influences how a user interacts with the AR workflow.
The spectrum of AR hardware is broad, offering options for different operational needs and budgets:
- Smartphones and Tablets: As the most common entry points into AR, modern mobile devices possess the necessary cameras, sensors, and processing power to run sophisticated AR applications. They are an excellent choice for pilot projects or less demanding tasks.
- Monocular Smart Glasses: Designed for a single-eye display, these devices are ideal for delivering simple notifications, checklists, and data snippets. They enable a heads-up, hands-free operation by allowing workers to view contextual information while maintaining focus on the task.
- Binocular Smart Glasses: For more complex and immersive applications, binocular glasses provide a stereoscopic 3D view. These devices are often purpose-built for demanding industrial environments, featuring ruggedized designs, safety certifications, and advanced sensors for precise spatial tracking.
The infographic below illustrates the fundamental flow of an AR workflow, from capturing the real world to processing data and displaying the final augmented view.
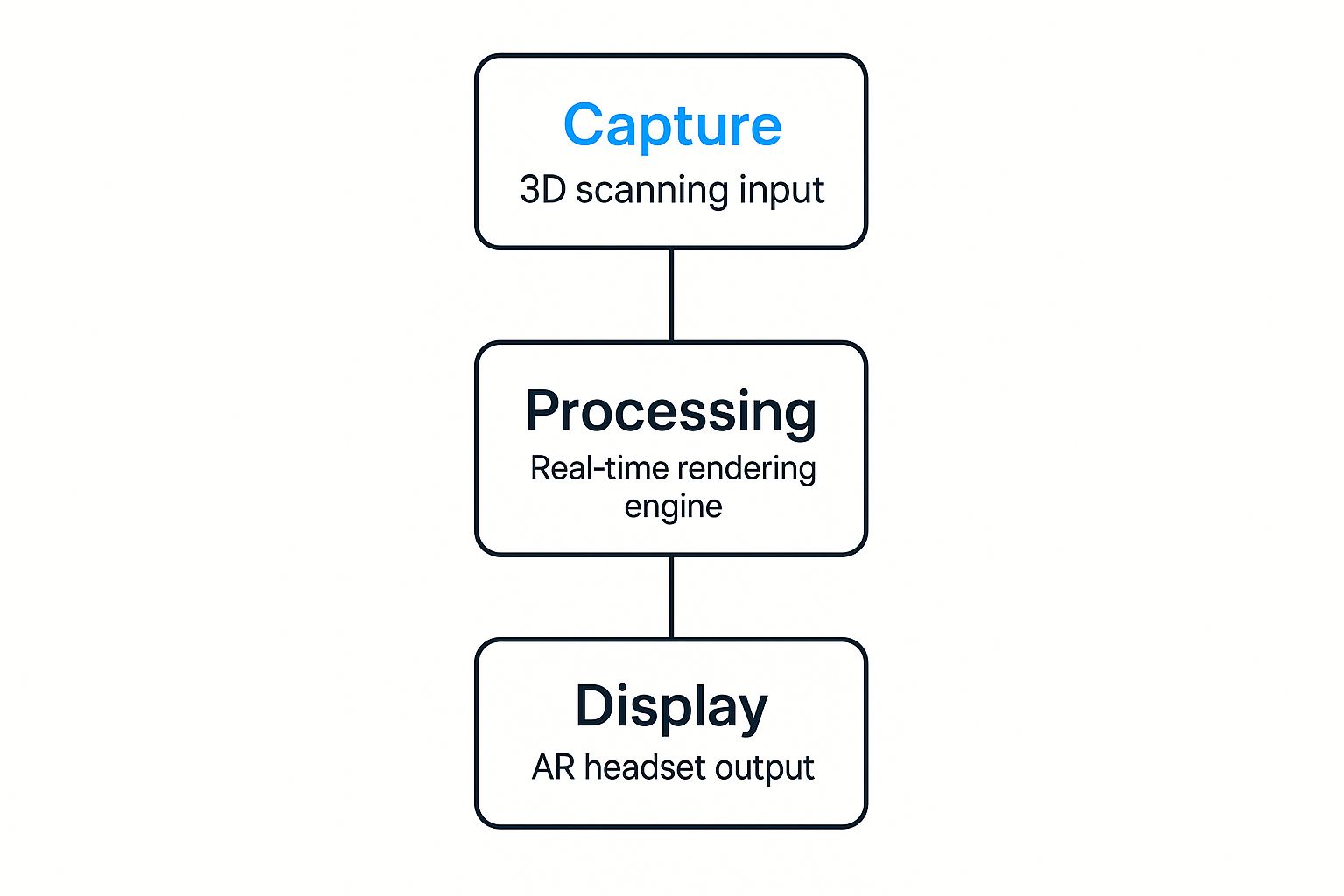
As shown, the hardware (capture and display) serves as the foundation of the entire process, making it a critical component for any effective implementation.
Software: The Brains of the Operation
If hardware is the body, software is the brain. It is the platform used to create, manage, and deploy AR content. Modern AR software platforms are increasingly user-friendly, many featuring low-code or no-code interfaces that empower subject matter experts—not just developers—to build powerful workflows.
A robust AR platform acts as a central nervous system. It connects the hardware with real-time data to create intuitive, guided experiences that translate raw information into clear, actionable visual instructions.
The software handles complex tasks such as rendering 3D models, tracking objects in the physical world, and managing user interactions. The integration of AI has significantly enhanced these capabilities. To learn more, you can explore how AI is revolutionizing AR technologies and making them smarter and more powerful.
Data: The Fuel for Contextual Insights
Finally, data is the fuel that powers the AR workflow. An AR application disconnected from business systems is like a GPS without live traffic updates—useful, but lacking critical real-time context. The most effective AR experiences are driven by dynamic information pulled directly from existing enterprise systems.
This data connectivity transforms a static 3D model into a live, interactive guide.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Pull up-to-date inventory levels, work orders, or compliance information directly into a user’s field of view.
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM): Access the latest CAD drawings, assembly instructions, or version histories to ensure technicians are always working with the correct specifications.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Stream live data from equipment sensors to display real-time performance metrics like temperature or pressure, enabling predictive maintenance and instant diagnostics.
By integrating with these data sources, an AR workflow becomes more than a simple visualization tool. It transforms into a dynamic decision-support system that provides frontline teams with the exact information they need, precisely when they need it.
Transforming Industries With AR-Powered Processes

The true value of an augmented reality workflow is realized when it transitions from concept to practical application. These AR-powered processes are delivering measurable results across diverse industries, not as futuristic experiments, but as practical solutions to today's business challenges.
From factory floors to remote field service locations, AR is changing how work is performed by providing frontline teams with the digital information they need to do their jobs more safely, quickly, and accurately.
Let’s examine a few real-world examples.
Streamlining Manufacturing and Assembly
In manufacturing, precision is a fundamental requirement. Traditional assembly lines often rely on paper manuals or operator memory, both of which can lead to human error, production delays, and lengthy training periods for new employees.
An AR workflow changes this paradigm. An assembly technician wearing smart glasses receives digital instructions projected directly onto their workstation, eliminating the need to look away to consult a screen or binder.
- Step-by-step guidance indicates the next part to be used and shows its exact placement.
- 3D animations illustrate complex movements, removing guesswork from intricate steps.
- Built-in quality checks can confirm correct part placement before the system allows the worker to proceed.
This interactive, heads-up guidance significantly reduces the cognitive load on the worker. The result is a substantial reduction in assembly errors, faster production cycles, and a more rapid ramp-up for new employees.
By overlaying digital blueprints and instructions directly onto the physical product, manufacturers achieve a level of accuracy and speed previously unattainable. It effectively turns every worker into an expert from their first day.
Optimizing Logistics and Warehousing
Warehouse operations are a constant race against time. Every second saved in order fulfillment contributes to faster delivery and improved customer satisfaction. However, navigating a large facility with a paper list or handheld scanner can be inefficient.
AR-guided "vision picking" offers a more intelligent approach. Warehouse staff wear smart glasses that provide visual cues directly in their line of sight.
- The system highlights the most efficient route to the correct aisle and bin.
- Upon arrival, the specific item to be picked is visually highlighted on the shelf.
- Integrated scanners can instantly confirm the pick, virtually eliminating shipping errors.
With this type of AR workflow, workers' hands remain free, and their eyes stay focused on the task. This simple change enhances both the speed and accuracy of the entire fulfillment process.
Empowering Field Service and Maintenance
For a field service technician, encountering an unfamiliar problem on-site is a worst-case scenario. It often results in multiple trips, extended equipment downtime, and customer dissatisfaction. AR transforms this dynamic through remote expert assistance.
When a technician encounters a challenge, they can use their AR device to initiate a video call, sharing their exact point of view with a senior expert located elsewhere. The remote expert can then:
- See what the technician sees in real time.
- Draw and annotate on the live video feed, with instructions that "stick" to the physical equipment in the technician's view.
- Push technical drawings or manuals directly into the technician's display.
This "see-what-I-see" support enables the diagnosis and resolution of complex problems on the first visit. It reduces travel costs for senior staff and, most importantly, returns critical equipment to service in a fraction of the time.
What Are the Real-World Payoffs of an AR Workflow?
Implementing an augmented reality workflow is a strategic business decision that yields tangible returns. Integrating AR delivers real, measurable improvements to the key performance indicators (KPIs) that are critical to operational success.
The core principle is simple: AR significantly reduces the "time-to-information." By projecting critical data, diagrams, and instructions directly into a worker's line of sight, it eliminates the wasted time spent searching for manuals, referencing separate screens, or waiting for expert assistance. This immediate access to knowledge creates a powerful ripple effect across the entire operation.
A Major Boost to Operational Efficiency
The first and most apparent benefit is a significant increase in efficiency. When frontline workers receive hands-free, step-by-step guidance overlaid on their work environment, their performance improves. Tasks that previously involved a clumsy juggle of tools, parts, and instructions become smooth, intuitive, and fast.
This translates directly into:
- Faster Job Completion: Studies consistently show that AR guidance can increase worker productivity by 30-50% in complex assembly and maintenance tasks.
- Reduced Downtime: When critical equipment fails, every second is costly. With AR, technicians can diagnose and resolve problems faster, minimizing downtime for valuable assets.
An augmented reality workflow minimizes cognitive load. It delivers the right information at the right time and place, freeing up workers to focus on the task itself. They spend less time searching and more time doing.
The market is responding to these benefits. The global AR/VR market is projected to reach $89.82 billion in 2025, a substantial increase from $62.75 billion in 2024. This rapid growth, representing a compound annual growth rate of 31.6%, is driven by companies realizing these tangible results. For more on this trend, review these augmented reality market insights.
Nailing Quality Control and Accuracy
Human error is a significant drain on profitability, leading to rework, wasted materials, and potential safety issues. An AR workflow is a powerful defense against this. It acts as a digital supervisor, providing clear visual guidance that eliminates guesswork.
When a technician sees a 3D model illustrating the precise alignment of a component, the probability of error decreases dramatically. This digital oversight ensures procedures are followed correctly every time, significantly improving first-time-right rates. The end result is a more consistent, higher-quality output and a stronger brand reputation.
Creating a Safer, More Compliant Workplace
In any industrial environment, safety is paramount. AR workflows contribute directly to a safer workplace by enabling hands-free operation. Teams can keep both hands on their tools and maintain focus on the task, rather than handling a tablet or binder.
Furthermore, AR systems can act as a proactive safety mechanism.
- Hazard Alerts: Digital warnings can appear in a worker's field of vision, highlighting a hot surface, a high-voltage area, or reminding them of required personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Built-in Checklists: Interactive safety checklists can be integrated into the workflow, requiring workers to confirm that all safety protocols have been followed before beginning a task.
Speeding Up Training and Closing the Skills Gap
Nearly every industry is facing a skills gap as experienced veterans retire and new hires require extensive training. AR fundamentally changes the training paradigm.
Immersive AR training allows new employees to learn complex jobs directly on the factory floor, guided by interactive digital instructions at their own pace. They are not just reading about a task; they are doing it in a safe, guided environment. This approach has been shown to reduce onboarding time by as much as 75%, transforming new hires into proficient team members far more quickly.
To understand how to track these improvements, review our guide on how to measure training effectiveness.
Impact of AR Workflows on Key Business Metrics
The table below summarizes the performance improvements that can be realistically expected from implementing an augmented reality workflow.
| Business Metric | Area of Impact | Potential Improvement Range |
|---|---|---|
| Productivity | Assembly, Maintenance, Field Service | 25-50% increase in task speed |
| Error Rate | Quality Control, Complex Assembly | Up to 90% reduction in errors |
| Training Time | Onboarding, Reskilling | 50-75% faster time-to-competency |
| Equipment Downtime | Maintenance & Repair | 20-40% reduction in downtime |
| Safety Incidents | All Industrial Operations | 15-30% reduction in incidents |
These figures are not just projections; they are the results companies are achieving today. By bridging the gap between digital information and the physical world, AR workflows unlock new levels of human potential and operational excellence.
Getting Your AR Strategy Right: A Practical Guide

Successfully implementing an augmented reality workflow requires more than just new technology; it demands a practical roadmap. A thoughtful strategy is what distinguishes a short-lived pilot project from a scalable solution that delivers lasting value.
The most effective approach is to focus on solving problems, not just deploying technology. Successful AR projects are problem-driven. Before considering specific hardware or software, identify a high-impact challenge within your operations. This grounds the project in business reality and provides a clear path to demonstrating a return on investment.
Start Small With a Focused Pilot Project
Avoid attempting a massive, company-wide rollout from the start. The prudent approach is to begin with a focused pilot project. The goal is to solve one well-defined problem and prove that an AR workflow can deliver value in a controlled environment. This provides an opportunity to learn, adapt, and build momentum for broader implementation.
Look for a process that is a known bottleneck or a consistent source of errors. Good candidates for an initial AR pilot often include:
- Complex Assembly Tasks: AR is ideal for these applications, where step-by-step visual guidance can reduce errors and increase production speed.
- Preventive Maintenance Checks: AR can provide interactive checklists and instructions to ensure technicians complete every required step correctly.
- New Hire Onboarding: Select a specific piece of equipment and use AR to train new team members, allowing for direct measurement of reduced training time and faster proficiency.
Focusing on a single use case creates a clear benchmark for success and makes it easier to measure the impact on metrics like task time, error rates, and productivity. This builds a solid business case for future investment. Exploring the various applications of augmented reality for industry can provide inspiration for where to begin.
Get Your Frontline Workers Involved From Day One
This is a critical step that is often overlooked. It is essential to involve end-users from the very beginning. Your technicians, operators, and assembly workers possess expert knowledge of the frustrations and inefficiencies of current processes.
An AR solution designed without input from the people who will use it is unlikely to succeed. For user adoption to occur, the tool must be intuitive, comfortable, and genuinely make their job easier—not add a new layer of complexity.
Engage with them early and maintain an open dialogue. Ask what information would be most helpful and how they would prefer to see it presented. Involving them in the process not only results in a better, more user-friendly tool but also fosters a sense of ownership, turning potential critics into advocates.
Build a Scalable Content Pipeline
An AR experience is only as good as the content that powers it. The 3D models, instructional videos, and step-by-step guides are the lifeblood of the workflow. It is a common mistake to underestimate the effort required to create and manage this digital content.
A scalable content pipeline should be planned from the outset. This means establishing a clear process for:
- Creating 3D Assets: Determine your approach. Will you utilize existing CAD models, create new ones, or use 3D scanners to digitize real-world objects?
- Authoring Instructions: Decide who will develop the step-by-step procedures. Empowering your own subject matter experts to create content using no-code platforms is often the most effective route.
- Managing and Updating Content: Processes evolve, and AR content must be kept current. A central content management system is essential for maintaining accuracy and controlling versions.
Plan for Solid Data Integration
To fully leverage the power of an AR workflow, it must be integrated with your other business systems. A standalone AR application is useful, but a connected one is transformative. Integration allows the AR solution to pull real-time data and present it exactly when and where your team needs it.
Consider connecting your AR platform to your ERP for work orders, your PLM for the latest schematics, or IoT sensors for live equipment data. This transforms a static instruction manual into a live, data-rich tool that supports smarter, on-the-fly decision-making, ensuring your AR solution grows with your business and delivers dynamic value.
Where Augmented Reality Workflows Are Headed Next
The growth of the augmented reality workflow is not slowing; it is accelerating. AR is evolving from a niche tool into a fundamental component of the industrial toolkit, integrated directly into daily operations.
This shift is driven by a powerful convergence with other key technologies, particularly Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT).
This is not merely about adding features; it's about creating truly intelligent systems. Consider a technician wearing smart glasses who sees not just a digital overlay of repair steps, but also live data streaming from IoT sensors on the machine. An AI analyzes this data in real time, predicts a potential failure before it occurs, and instantly generates a new AR workflow to prevent it.
This represents a monumental leap from reactive to predictive assistance. Instead of just showing a worker how to fix what is broken, the system will anticipate problems and deliver proactive, context-aware instructions to prevent them from happening.
This level of intelligent guidance fundamentally changes the nature of frontline work, empowering every employee to become a highly skilled, data-driven decision-maker.
Next-Generation Hardware and Mass Adoption
The rapid pace of AR hardware development is a major catalyst for this future. Upcoming devices will be sleeker, more powerful, and lighter, resembling standard safety goggles.
As manufacturing scales and the technology matures, these devices will also become more affordable. This price reduction will be a tipping point for many organizations, making it feasible to equip entire teams. At that point, the augmented reality workflow will become the standard method for everything from training and maintenance to remote collaboration.
The future of work is not about replacing people with technology, but about amplifying human capabilities. The AR-enhanced workforce is already a reality, and its potential is expanding daily. The companies that begin their AR journey now are not just adopting a new tool—they are building a foundational competitive advantage that will define their success for years to come.
Common Questions About AR Workflows
When first exploring the implementation of an augmented reality workflow, it is natural to have questions. For most business leaders and project managers, understanding the practical aspects of AR is the first step toward a successful rollout.
Let’s address some of the most common questions from companies considering AR adoption.
Where’s the Best Place to Start an AR Project?
Always begin with a real, high-impact business problem. Avoid adopting technology for its own sake. Instead, identify a single, measurable challenge that has been a persistent operational issue.
Good candidates often include complex assembly tasks with high error rates, critical maintenance procedures with no margin for error, or the need to accelerate the onboarding of new technicians.
By focusing on one specific use case, you can execute a controlled pilot project. This is the most efficient way to demonstrate the value of AR and build a strong business case for broader implementation.
What Really Drives the Cost of Implementation?
The investment for an augmented reality workflow varies but is primarily influenced by four key factors:
- Hardware Selection: Costs can be minimal if using existing smartphones and tablets, or more significant if specialized industrial smart glasses are required.
- Software and Licensing: This includes the AR platform itself, typically offered through subscription-based (SaaS) models, though on-premise solutions are also available.
- Content Creation: The complexity of your 3D models and work instructions will influence the initial setup cost. More detailed and interactive content requires a larger investment.
- Integration Needs: If the AR platform needs to interface with existing systems—such as an ERP or PLM—the cost of that integration work will be part of the overall investment.
How Much Training Will Our Team Actually Need?
Significantly less than one might expect. Modern AR solutions are designed to be highly intuitive, which reduces training time. The objective is to make the technology a natural extension of the job, not another complex tool to master.
Most of the "training" involves familiarizing users with the hardware and navigating the software interface.
The core principle of an effective augmented reality workflow is that it simplifies tasks, not complicates them. The system itself should guide the user, eliminating the need for extensive technical expertise.
Typically, frontline workers can become proficient with a new AR tool within a few hours. The system itself serves as an on-the-job training partner, facilitating real-time skill development.
At AIDAR Solutions, we create immersive AR applications that tackle real industrial problems, boosting efficiency and making training stick. Learn how our tailored AR workflows can transform your operations.


