Augmented Reality Remote Assistance: A Complete Business Guide
Picture this: your most experienced expert is instantly "there" to guide a junior technician through a complex repair, seeing exactly what they see in real-time. This is the simple, yet profound, power of augmented reality remote assistance—a technology that merges the digital and physical worlds to solve problems on the spot. It elevates a standard video call into a fully interactive, hands-on support session.
What Is AR Remote Assistance?

At its core, AR remote assistance is a tool that lets an expert guide a field technician from anywhere in the world. The person on-site simply uses a smartphone, tablet, or smart glasses to share their real-world view with the remote specialist.
The expert can then overlay digital information—like instructions, arrows, or diagrams—directly onto that live video feed. This allows the expert’s "digital hands" to point out the exact button to press or the specific wire to check, eliminating guesswork and miscommunication.
From Downtime to Uptime
Consider a common industrial challenge: a critical machine on the factory floor suddenly grinds to a halt. Traditionally, this initiated a costly, time-consuming process. The factory would need to schedule a visit from a specialized technician who might not be available for days, all while production losses mount.
With AR remote assistance, that scenario is fundamentally different. An on-site operator can immediately connect with a remote expert. The expert sees the machine through the operator's device and can guide them through diagnostics and repairs in real time.
This technology collapses a multi-day delay into a quick, first-time fix. It is a proven tool that empowers your workforce, reduces downtime, and solves real operational challenges today.
The Core Components of AR Assistance
This powerful collaboration is made possible by a few key components working in harmony.
- Shared Visual Context: A live video stream from the field technician's device creates a common ground, ensuring both parties are looking at the exact same problem.
- Interactive Annotations: The remote expert can draw, place arrows, and share documents directly onto the worker’s screen. The instructions are clear and unambiguous.
- Real-Time Communication: Integrated voice and text chat keep the conversation flowing naturally, making the process feel efficient and collaborative.
This technology is a powerful way to bridge the skills gap, connecting your most knowledgeable team members with those who need their guidance, no matter their location. The applications extend beyond repairs, touching everything from operational procedures to onboarding. By providing this instant access to expertise, you’re also building a more resilient and capable team. For more on how this applies to employee development, you can learn about augmented reality and training.
How The Technology Works in Practice
Let’s move from theory to a practical scenario. Sarah, a field service engineer, is facing a complex piece of industrial machinery that has stopped working. The traditional method meant waiting days for a specialist to arrive. Now, she simply uses her tablet.
With a few taps on a specialized AR application, Sarah initiates a call with David, a senior expert located in his office hundreds of miles away. This isn't just a video call—it’s the start of a shared, interactive work session.
Establishing a Shared Reality
First, they establish a shared visual context. Sarah points her tablet's camera at the machine, and a live video stream instantly appears on David's monitor. He sees exactly what she sees, in real-time, eliminating the frustrating back-and-forth of describing a complex technical problem over the phone.
This live feed is the canvas for the entire AR experience. From here, David can start interacting with Sarah's environment as if he were standing right beside her.
The core of the technology is this shared visual stream. It transforms a one-way observation into a two-way collaboration, where the remote expert can actively participate in solving the problem rather than just passively listening to a description.
Using his mouse or a touchscreen, David can place digital annotations directly onto the live video. These are not flat drawings; they are 3D objects that "stick" to the real-world components Sarah is looking at, even as she moves.
- Anchored Arrows: David can place a bright, 3D arrow pointing to a specific valve that needs to be checked. When Sarah moves her tablet, that arrow stays locked onto the valve, leaving no room for doubt.
- Step-by-Step Instructions: He can create a sequence of numbered markers on the machine's control panel, showing Sarah the exact order of operations for a diagnostic test.
- Diagram Overlays: For more complex issues, David can pull up a technical schematic and overlay it onto a specific part of the machine. This lets Sarah compare the diagram directly with the physical hardware in front of her.
The Key Technological Components
This seamless interaction is powered by three key components working together.
- The Hardware: The technician on-site needs a device with a camera. This could be a modern smartphone or tablet, or more advanced hardware like smart glasses for a hands-free experience. The remote expert only needs a computer or tablet.
- The Software Platform: This is the application that facilitates the entire process. The software handles the video stream, communication, and all the AR annotations.
- The Network Connection: A reliable internet connection (Wi-Fi, 4G, or 5G) is the pipeline that carries the high-quality video and data needed for a smooth, lag-free session.
Together, these elements create a collaborative environment that’s both powerful and intuitive. The technology has evolved rapidly, and recent developments have made these tools more precise and accessible than ever. For instance, AI-driven virtual assistants have improved AR tool accuracy by approximately 20%, enhancing the user experience. Additionally, cloud-based deployments now constitute 55% of AR remote support systems, offering the flexible, scalable solutions that enterprises require. You can explore more data on the growth of the AR remote assistance market on globalgrowthinsights.com.
This practical, see-what-I-see approach removes guesswork, reduces the risk of human error, and significantly speeds up troubleshooting and repairs. The on-site technician is no longer working alone—they are supported by the real-time expertise of a seasoned professional.
The Real-World Payoff: Core Business Benefits of AR

Understanding how augmented reality remote assistance works is one thing, but seeing how it directly impacts the bottom line is what drives adoption. This isn't about futuristic technology for its own sake; it’s about delivering powerful, measurable advantages that transform how a business operates.
These benefits create tangible value across three critical pillars of any industrial operation: efficiency, cost savings, and knowledge transfer.
By moving beyond the limitations of simple video calls, AR adds an interactive digital layer that boosts productivity. When you can visually guide a technician step-by-step, you eliminate guesswork and reduce the time it takes to diagnose and fix a problem. This contributes to a significant increase in first-time fix rates—a critical KPI for any service organization.
Supercharging Operational Efficiency
The most immediate impact of AR remote assistance is an improvement in speed and accuracy. When a machine goes down, every minute of downtime translates to lost revenue. AR collapses the problem-solving timeline by giving your on-site team instant access to expert guidance.
Instead of waiting days for a specialist to travel, an on-site technician gets real-time support, complete with visual instructions overlaid on their physical workspace. This gets equipment back online faster and drastically reduces the chance of errors that lead to repeat visits.
Properly implementing AR can be a cornerstone of a solid operational excellence framework, helping to streamline processes and improve output.
AR remote assistance directly targets operational bottlenecks. By empowering frontline workers with expert knowledge on demand, companies can see dramatic reductions in equipment downtime and service resolution times.
This efficiency gain isn’t just for emergencies. Routine inspections, complex assemblies, and preventative maintenance tasks all become faster and more accurate. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on how businesses are using augmented reality for maintenance to overhaul their workflows.
Delivering Hard Cost Savings
The financial case for augmented reality remote assistance is incredibly compelling, starting with a massive reduction in travel expenses. Dispatching senior experts to different sites is a significant cost when factoring in flights, hotels, and lost productivity during transit.
With AR, the same expert can support multiple technicians in different cities—or even countries—on the same day, all without leaving their office. This shift leads to immediate and substantial savings, often delivering a surprisingly fast return on investment.
- Slash Travel Costs: Reduce the budget for expert site visits by up to 75% or more.
- Cut Downtime Losses: Faster repairs mean less production loss, which directly protects revenue.
- Optimize Your Experts: Senior staff can spend their time solving high-value problems instead of sitting in airports.
Impact of AR Remote Assistance on Key Business Metrics
The table below breaks down the direct and indirect benefits your organization can expect when implementing an AR remote support solution, tying the technology directly to financial and operational outcomes.
| Benefit Area | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Operational Efficiency | Reduces time-to-resolution for maintenance and repairs by providing instant, visually guided expert support. | 25-50% reduction in equipment downtime. Increased First-Time Fix Rates by 20-35%. |
| Cost Reduction | Eliminates the need for expert travel to on-site locations, lowering associated expenses for flights, lodging, and per diems. | Up to 75% reduction in annual travel budgets. Faster ROI, often within 6-12 months. |
| Knowledge Transfer | Captures expert knowledge during sessions and provides on-the-job training for junior technicians, mitigating skill gaps. | 40% faster onboarding for new technicians. Creates a reusable digital library of standard operating procedures. |
| Safety and Compliance | Allows experts to remotely guide technicians through hazardous tasks, ensuring procedures are followed correctly. | Reduction in workplace accidents and compliance-related incidents. Improved audit trails. |
As you can see, the value extends beyond simply fixing things faster. It strengthens the entire operational fabric of the company, making it more resilient, efficient, and profitable.
Accelerating Knowledge Transfer and Bridging the Skills Gap
Beyond the immediate financial wins, AR is an incredibly powerful tool for upskilling your workforce. As experienced veterans retire, they take decades of institutional knowledge with them. AR offers a practical way to capture that expertise and pass it on to the next generation of technicians.
During a remote assistance call, a junior employee receives one-on-one coaching from a seasoned professional. This on-the-job training is highly effective because it's contextual and applied to a real-world problem.
Furthermore, these sessions can be recorded to create a permanent library of training videos. New hires can watch a real expert solve the exact problem they're facing, ensuring critical knowledge remains within your organization. This creates a continuous learning loop that builds a more capable and self-sufficient team for the long haul.
Where AR Remote Assistance is Making a Real-World Impact
While the theory is compelling, the true value of augmented reality remote assistance is demonstrated when it solves complex, real-world problems. Across different industries, this technology is quickly moving from a novelty to an indispensable tool for maintaining complex machinery, ensuring quality, and making dangerous jobs safer.
The core principle is always the same: connect the person on-site with an expert elsewhere, placing them both in the same visual, interactive space. Let's examine how this plays out in a few demanding environments, turning potential disruptions into quickly managed tasks.
Streamlining Complex Manufacturing and Assembly
Imagine a new robotic arm on your production line grinds to a halt. Your local maintenance crew has never seen this model before, and flying in the manufacturer’s specialist means days of downtime and lost production. This is a classic scenario where AR remote assistance proves its worth.
Instead of waiting, an on-site technician can start a video call with the specialist, showing them a live feed of the robotic arm. From there, the remote expert can:
- Overlay Schematics: Project a digital blueprint directly onto the physical machine, so the technician can see exactly which part is which.
- Guide Diagnostics: Use 3D arrows and markers to point to specific sensors or ports that need testing, walking the technician through a troubleshooting process.
- Demonstrate Repairs: Draw on the screen to show exactly how to recalibrate a joint or replace a faulty part, leaving no room for misunderstanding.
What could have been a multi-day shutdown can often be resolved in less than an hour. This rapid problem-solving is why the manufacturing and automotive sectors have increased their use of AR remote assistance tools by 35%. The technology’s troubleshooting capability is a significant factor, with North America leading adoption due to its deep roots in aerospace and defense. You can explore more data about the expanding AR remote assistance market on businessresearchinsights.com.
Enhancing Safety in the Energy Sector
The energy industry relies on some of the world's most critical—and dangerous—infrastructure, such as offshore wind turbines, remote pipeline stations, and sprawling refineries. Sending personnel to these locations for inspections or repairs is expensive, time-consuming, and carries inherent safety risks.
AR remote assistance changes that equation by allowing a single, less-experienced technician to perform the job under the virtual supervision of a senior engineer who is safely located back at the office.
By giving an expert "eyes on the ground" without the physical risk, AR fundamentally changes safety protocols. It ensures that complex procedures are followed correctly, even under pressure.
For example, during a wind turbine inspection, a remote expert can guide a technician through a pre-flight checklist for a drone. They can then annotate the live drone footage to highlight a potential stress fracture on a blade and confirm all safety measures are being followed. This not only improves the inspection quality but also creates a perfect digital record for compliance and audits.
Precision in Medical Technology and Healthcare
In the high-stakes world of medical technology, there is no room for error. When a complex surgical robot or a new diagnostic machine is being installed or repaired, precision is paramount. Traditionally, this requires flying a product specialist to the hospital to oversee the work.
AR remote assistance provides a powerful and immediate alternative.
- Guided Installation: A factory expert can remotely guide a hospital's biomedical engineer through the complex setup of a new MRI machine, ensuring every connection and setting is correct.
- Surgical Support: During a difficult procedure, a surgeon wearing AR smart glasses can consult with a world-renowned specialist, receiving real-time advice and diagrams overlaid directly onto their view of the patient.
- Device Maintenance: A field technician can receive step-by-step visual instructions to service sensitive lab equipment, which drastically reduces the chance of a costly mistake and ensures the device performs to specification.
These field examples all point to one conclusion: AR remote assistance is about getting the right expertise to the right place at exactly the right time. The tools are especially transformative for any augmented reality field service team trying to boost their first-time fix rates and improve customer satisfaction. By closing the gaps created by distance and knowledge, this technology helps teams get the job done safer, faster, and more effectively.
Your Roadmap to Implementing AR Solutions
Adopting augmented reality remote assistance may seem like a large undertaking, but it is a manageable process with a clear roadmap. By breaking the implementation down into structured steps, any company can move from initial curiosity to a full-scale deployment that delivers tangible value. A well-planned roadmap ensures you address the right challenges, achieve team buy-in, and measure meaningful results from day one.
It all starts with a smart, focused pilot project. The goal is to prove the technology's worth on a small scale before committing to a full rollout.
This visual shows the simple, yet powerful, workflow of an AR service call—from the first request to the final fix.
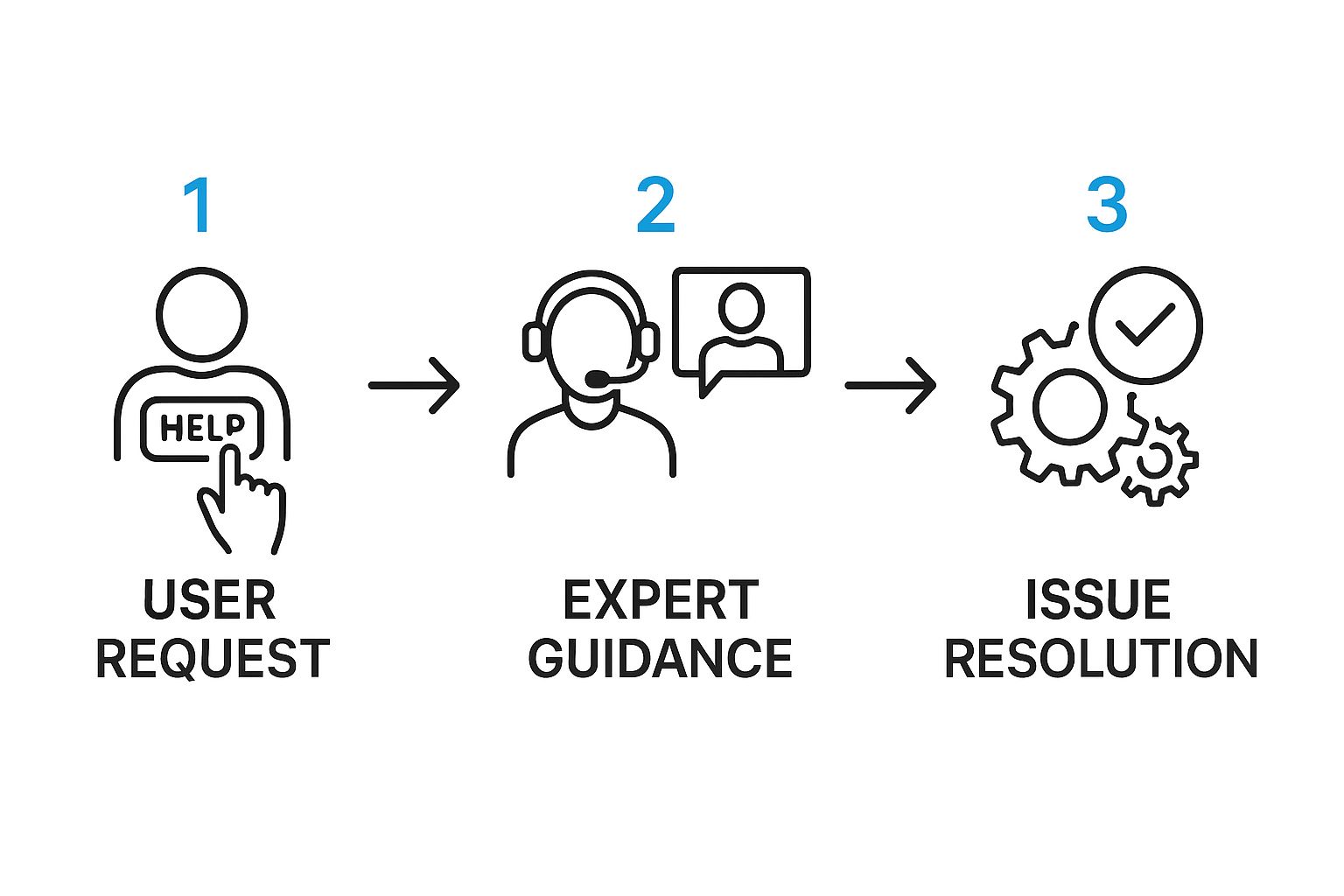
It's a perfect example of how AR remote assistance cuts through communication barriers to get expert help exactly where it's needed.
Phase 1: Identify a High-Impact Pilot Project
First, this is not about overhauling your entire operation overnight. The key to a successful rollout is to identify a single, high-impact area where AR can solve a persistent and expensive problem. This focused approach makes it much easier to demonstrate a clear return on investment.
Look for situations that involve high travel costs for experts, costly equipment downtime, or a significant skills gap between new technicians and seasoned veterans. A classic example is a manufacturing line where one particular machine is a known bottleneck.
A successful pilot serves as your internal case study. It provides hard data and a compelling story to win over stakeholders and build momentum for a company-wide deployment.
To begin, assemble a small, cross-functional team. Ensure you have representation from IT, operations, and a couple of field technicians. Their hands-on experience is invaluable for pinpointing the ideal use case and defining what success looks like.
Phase 2: Select the Right Tools for the Job
Once you have a pilot project scoped out, it's time to select your hardware and software. A great advantage of modern AR solutions is their flexibility. You don't always need expensive, specialized equipment to get started—many platforms work perfectly on the smartphones and tablets your team already uses.
For more intensive, hands-free work, you can begin to evaluate smart glasses. When choosing a software platform, focus on features that align with your pilot's goals, such as intuitive annotation tools, session recording for training purposes, and simple integration with your existing systems.
- Define Hardware Needs: Will standard mobile devices suffice, or do you need a hands-free solution like smart glasses for the task?
- Evaluate Software Features: Look for a platform with robust annotation tools, a user-friendly interface, and strong security protocols.
- Consider Connectivity: Assess the network reliability where your pilot will take place. While connectivity is improving globally, it can still be a challenge. For instance, over 40% of companies in developing nations cite connectivity as a major barrier, underlining the importance of a stable network.
Phase 3: Execute a Successful Trial Program
Now it is time to put the technology to the test. A successful trial is built on three pillars: clear goals, effective training, and tracking the right data. Before you begin, define the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) you will use to measure success.
Be specific. For example, you could track the reduction in average repair time, the increase in first-time fix rates, or the total travel costs saved during the pilot.
Training is also a critical element. You need to ensure everyone involved feels comfortable and confident with the new tools. Often, a brief, hands-on workshop is all it takes to get them up to speed and genuinely enthusiastic about the possibilities.
Phase 4: Create a Strategy for Scaling
Once your pilot program has clearly demonstrated its value, the final step is to map out a strategy for rolling out the solution across the rest of the organization. Use the data and success stories from your trial to build a solid business case for a wider implementation. For more ideas on this, reviewing proven field service management best practices can provide a strong foundation for your expansion.
Your scaling strategy should outline a phased rollout, identify which teams or departments are next in line, and create a standard training process for all new users. By taking a step-by-step approach, you can turn a successful pilot into a true competitive advantage for your entire business.
The Future of Remote Collaboration

The evolution of augmented reality remote assistance is only just beginning. It is rapidly moving beyond simple real-time video calls to become a smarter, more predictive tool that is deeply integrated into a company’s operations. The next wave of this technology will push even more intelligence directly into the technician's line of sight.
Imagine a system that not only shows what an expert is pointing at but also anticipates problems before they happen. That is the direction we are headed. Deeper AI integration, fueled by real-time data from the Internet of Things (IoT), will soon be flagging potential equipment failures before a critical breakdown ever occurs.
Smarter Tools and Richer Data
The next generation of AR solutions is all about data fusion. Consider a field engineer looking at a pump and instantly seeing its live pressure, temperature, and vibration levels displayed as a clean digital overlay. This kind of immediate insight, pulled from IoT-enabled machinery, completely changes the approach to maintenance, turning it from a reactive task into a proactive strategy.
This blend of technologies creates a powerful new reality for frontline workers. Suddenly, every piece of equipment can provide its operational history and current health on demand. To get a better sense of how these interactions fit into a bigger picture, it's worth exploring the broader landscape of future customer collaboration.
Investing in augmented reality remote assistance is no longer just about solving today's problems. It's about building a more resilient, efficient, and data-empowered workforce for tomorrow.
The hardware is also keeping pace. Smart glasses are becoming lighter, more powerful, and comfortable enough for all-day use. These improvements are making hands-free operation the new standard, which is a massive benefit for both productivity and safety in complex work environments.
A Market Poised for Growth
The financial forecasts for the AR remote assistance software market show a clear and aggressive upward trend, signaling that this is becoming a core industrial technology.
One analysis, for example, projects the market will grow from USD 1.5 billion to approximately USD 7.0 billion by 2033. That level of compound annual growth is driven by tangible business value.
This growth is more than just a number on a chart; it represents a fundamental shift in how industries handle operational support, training, and knowledge sharing. By adopting these tools now, businesses are not just keeping up—they are laying the groundwork for a more intelligent and connected future.
Still Have Questions? We've Got Answers.
When considering the adoption of any new technology, it is natural for questions to arise. Business leaders and IT managers often have practical concerns, so let's address some of the most common ones regarding augmented reality remote assistance.
What Kind of Hardware Do We Need?
Getting started is likely easier than you think. Most modern AR assistance platforms are designed to run on the devices your team already possesses—such as standard smartphones and tablets. This flexibility makes the initial rollout straightforward and helps contain costs.
For more complex jobs where a technician requires both hands to be free, specialized AR smart glasses offer significant advantages. The right choice always depends on the specific task and the work environment.
How Does This Fit with Our Current Software?
Integration is a key consideration, and today's AR solutions are built for interoperability. Most platforms come with robust APIs that allow them to connect directly with your existing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) or Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems.
This connectivity is crucial. It creates a seamless, two-way flow of data, allowing technicians to pull up work orders or log session notes directly within the AR application. This eliminates clunky data entry and prevents information from becoming siloed.
Is It Secure?
Absolutely. Security is a core design principle, not an afterthought. All data transmitted during a remote session—from video and audio feeds to any shared files—is typically protected with end-to-end encryption.
This means your sensitive operational information remains confidential and is protected from unauthorized access, meeting the stringent security standards that enterprises demand.
What Happens if the Internet Connection is Bad?
Field conditions are rarely perfect. While a strong connection is always ideal, leading AR tools are designed for real-world scenarios. They often feature a low-bandwidth mode that automatically optimizes the video stream to maintain functionality, even on a weak signal.
Additionally, you'll find features like the ability to freeze the video and annotate a crisp, high-resolution snapshot. This ensures that even if the live stream becomes choppy, the expert can still provide crystal-clear instructions.
Ready to give your teams the power of instant expert guidance? AIDAR Solutions provides powerful augmented reality remote assistance tools that slash downtime and supercharge efficiency. See how AIDAR.SERVICE can change the way you work by visiting us at https://aidarsolutions.com.



Comment(01)