A Practical Guide to Augmented Reality for Industry
Picture a veteran engineer’s lifetime of knowledge projected as a visual guide onto a complex machine for a new hire. That is the real-world power of augmented reality for industry. This is not a distant concept; it is a hands-on tool that is already closing the gap between digital information and physical work, solving critical industrial challenges today.
What Is Augmented Reality in an Industrial Context?

At its core, augmented reality layers digital information over your view of the physical world. It differs from virtual reality, which immerses you in a completely computer-generated space. AR adds useful context to what is already in front of you.
Think of it as a dynamic, intelligent overlay—a smart assistant that can provide instructions, highlight the exact part to fix, or display live data right where you are looking. This gives your team the exact information they need, precisely when they need it, leading to a workforce that can handle complex jobs faster, more accurately, and with greater safety.
Bridging the Digital and Physical Worlds
Industrial settings are filled with data—CAD files, assembly diagrams, real-time sensor readings from IoT devices, and more. Traditionally, accessing that information required a worker to stop, walk to a terminal, or consult a dense manual. This constant stop-and-start process is a major source of inefficiency and human error.
Industrial AR solves this problem by creating a seamless link between your digital database and your on-the-ground workforce.
- Real-Time Data Visualization: A technician can look at a pump and instantly see its current pressure, temperature, and vibration levels, enabling them to spot problems before a failure occurs.
- Interactive Work Instructions: Instead of reading a manual, an assembly line worker follows a 3D holographic guide that shows them exactly how to piece together a complex component, reducing training time and mistakes.
- Remote Expert Guidance: A field technician facing a difficult repair can stream their point-of-view to a senior expert thousands of miles away. That expert can then draw digital annotations directly onto the technician's view to guide them through the solution.
Augmented reality is not about replacing skilled people; it is about amplifying their skills. It puts the entire organization's collective knowledge at every employee's fingertips, effectively turning every team member into an expert.
Setting the Stage for Operational Excellence
By embedding digital insights directly into the workflow, AR addresses some of the biggest challenges in modern industry. It is a powerful tool for closing the skills gap, making difficult tasks easier to learn and perform correctly. It also boosts safety by visually flagging hazards and ensuring everyone follows the right procedures, every time.
From the factory floor to remote service calls, the use cases are broad. To better understand its applications, you can explore the many augmented reality industrial applications that are actively reshaping how companies operate. In the rest of this guide, we will detail how this technology delivers tangible results and what is required for implementation.
How AR Delivers Measurable Business Value
The concept of layering digital information onto the real world is impressive, but for any industrial operation, the adoption of new technology ultimately depends on its return on investment (ROI). The real power of augmented reality for industry lies not in its novelty, but in the concrete, measurable improvements it brings. This is a strategic investment that directly boosts efficiency, quality, and safety.
Consider the hidden costs of inefficiency, such as a technician searching through a binder for a schematic or a new hire constantly interrupting a senior colleague. AR streamlines these processes. By providing workers with the exact information they need, when they need it, tasks are completed faster and more accurately.
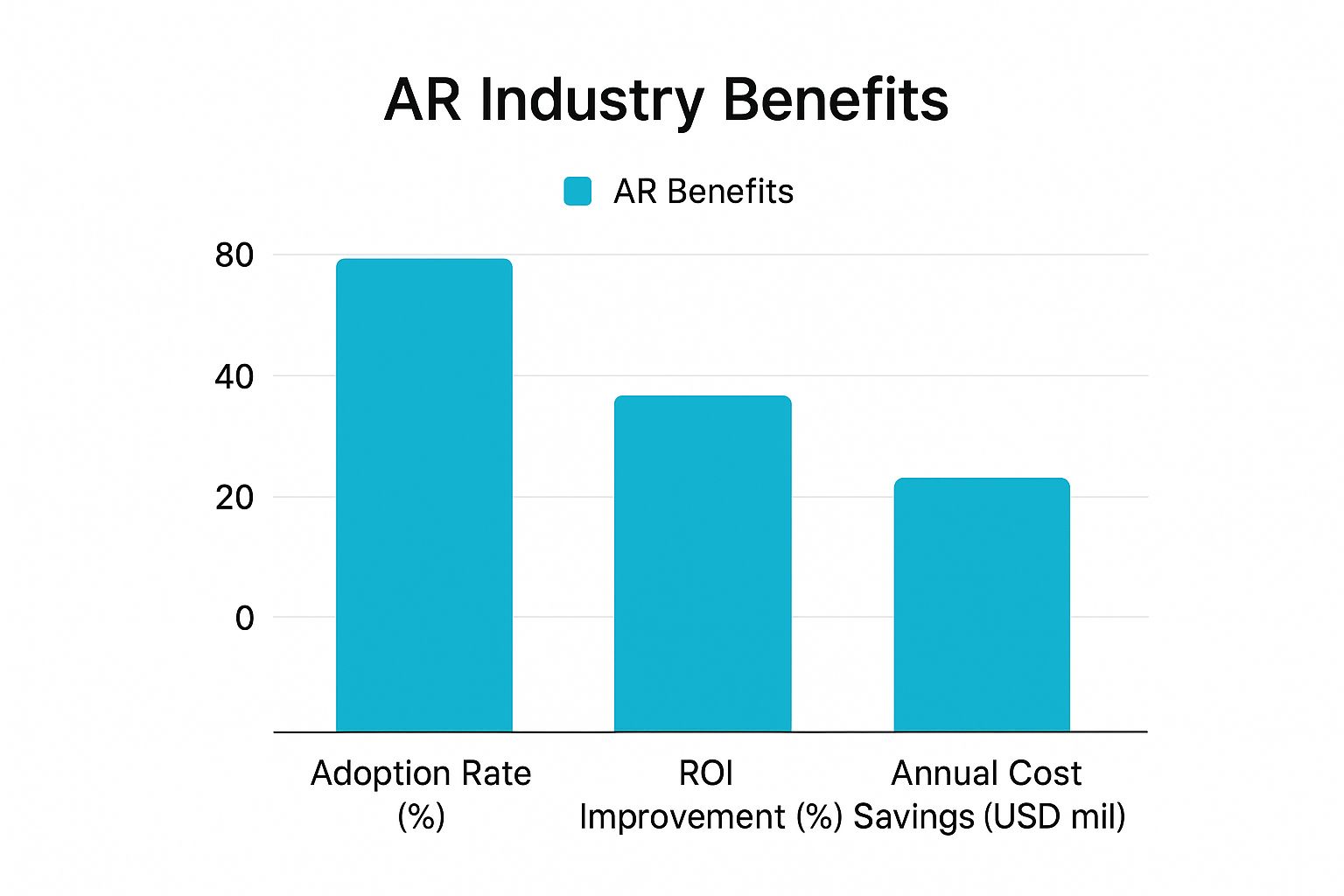
This direct impact is why the market is growing so rapidly. The global AR market has reached USD 83.65 billion, with the industrial and manufacturing sectors leading adoption. Companies are reporting up to 40% faster task completion and reducing assembly errors by 30% or more using AR for applications like remote assistance and machinery visualization. For a deeper analysis, refer to this detailed research on augmented reality.
The table below breaks down some of the most common benefits and their real-world impact.
Key Industrial AR Benefits and Their Impact
This table quantifies the practical benefits of AR implementation across key industrial metrics, providing a clear snapshot of its business value.
| Benefit Area | Description | Reported Improvement Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Operational Efficiency | Reduces time spent on tasks by providing instant access to information and step-by-step guidance. | Up to 40% faster task completion. |
| Error Reduction | Minimizes mistakes in assembly, maintenance, and quality checks through visual overlays and guided workflows. | Up to 90% reduction in human errors during assembly. |
| Training & Onboarding | Accelerates the learning curve for new employees with interactive, on-the-job training modules. | 30-50% reduction in training time. |
| Machine Downtime | Enables faster diagnostics and repairs through remote expert assistance, getting equipment back online quicker. | Up to 75% decrease in machine downtime. |
| Worker Safety | Highlights potential hazards and ensures compliance with safety protocols through real-time alerts. | Significant reduction in workplace accidents and safety incidents. |
These figures demonstrate that AR delivers substantial improvements in core business operations.
Driving Operational Efficiency
One of the first observable benefits of AR implementation is a significant increase in operational speed. When a technician sees repair instructions overlaid directly onto equipment, or an assembly worker follows a 3D guide, the workflow becomes more fluid with fewer stops, questions, and delays.
This is where the true value begins to emerge.
AR-powered remote assistance is a prime example. Instead of flying a specialist to a site—and waiting days for their arrival—a local technician can use an AR headset to share their view. The expert, from hundreds of miles away, can annotate the live video feed, circling the exact component to fix and guiding the entire process in real-time.
This "see-what-I-see" capability is transformative. It facilitates problem-solving in minutes, not days, which directly reduces machine downtime—a primary cause of revenue loss in manufacturing.
Improving Quality Control and Reducing Errors
Human error is a costly reality in any complex industrial job. AR addresses this by standardizing workflows and providing visual confirmation at every critical step.
- Guided Assembly: Technicians can follow animated sequences showing exactly where each part goes. This ensures every unit is built to specification and drastically cuts down on rework.
- Digital Checklists: Instead of a clipboard, workers can confirm tasks with voice commands or simple gestures, creating an automatic, error-proof audit trail for quality assurance.
- Error Detection: When connected to IoT sensors, AR devices can instantly flag a component that is overheating or out of tolerance, allowing for a fix before a defective product leaves the station.
Enhancing Worker Safety and Knowledge Retention
Beyond speed and accuracy, AR also helps create a safer work environment. A system can automatically highlight hot surfaces or high-voltage areas in a worker's line of sight. It can also integrate safety checklists directly into the workflow, ensuring procedures are followed correctly.
AR is also essential for knowledge transfer. As experienced veterans retire, their expertise can be captured and converted into interactive, AR-guided training modules. This not only brings new hires up to speed faster but also preserves critical institutional knowledge. When you view AR as a strategic enabler, not just a tool, you are building a more resilient and skilled workforce for the future.
Seeing AR in Action: Real-World Use Cases
The power of industrial AR becomes clear when moving from theory to the factory floor. This technology is currently used in manufacturing plants, remote field sites, and training centers to solve longstanding operational problems. The goal is to provide workers with the exact digital information they need, right when and where they need it.

Let's explore four practical examples where AR is making a significant difference, turning complicated jobs into simple, repeatable, and accurate processes.
Untangling Complex Assembly with Digital Work Instructions
Building a complex piece of machinery involves hundreds of parts, confusing paper manuals, and a high probability of error. The process is slow, tedious, and requires extensive training.
Now, imagine a technician wearing an AR headset. They see a 3D hologram of the next step projected directly onto their workstation. This is AR-guided assembly. The system indicates which part to grab, shows precisely where it goes, and can even display the correct torque setting for a bolt.
- Step 1: A 3D model of the product appears, highlighting the first part in the sequence.
- Step 2: Once the technician fits the part correctly, the system confirms it and highlights the next one.
- Step 3: For complex steps, short animations demonstrate the procedure, eliminating guesswork.
This transforms assembly from a memory-based task into a live, visually guided process. Companies using this have seen first-time quality rates increase dramatically, reducing rework costs and onboarding new hires in record time.
The result is near-perfect accuracy, even for workers unfamiliar with a specific product. In industries like aerospace and automotive manufacturing, where a single mistake can be catastrophic, this level of consistency is invaluable.
Taking the Guesswork Out of Maintenance and Repairs
When a machine breaks down, maintenance teams often have to shut it down and begin disassembly just to diagnose the problem, leading to significant wasted time and lost production.
Industrial AR offers a more intelligent approach. A technician can point a tablet at a machine or look through smart glasses to "see inside" it. A digital twin of the equipment is overlaid on the real thing, showing internal components and pulling in live sensor data.
- Quick Diagnosis: A technician can instantly spot a valve with a pressure problem or an overheating bearing without opening a single panel.
- Guided Fixes: Once the issue is identified, the AR system projects step-by-step repair instructions directly onto the machine, pointing out the exact components that need service.
This drastically reduces diagnostic time and gets production back online faster. Technicians arrive knowing the problem and with the right tools, turning a multi-hour issue into a quick, targeted fix.
Getting Expert Help, Instantly and Remotely
When a critical machine fails at a remote facility and the local technician lacks the necessary expertise, the only option has traditionally been to fly in a senior expert, a delay that can cost thousands in lost revenue.
AR-powered remote assistance changes this scenario. The on-site worker wears an AR headset and video calls an expert who could be anywhere in the world. The expert sees exactly what the technician sees in real-time.
From their desk, the expert can draw on the technician's screen, place arrows on specific parts, and display schematics that appear anchored in the technician's real-world view. This "see-what-I-see" support solves complex problems in minutes instead of days, closing skills gaps on the spot.
Building a Safer, More Confident Workforce with Immersive Training
Training new hires on heavy or dangerous machinery presents challenges. On-the-job training can be risky and ties up production equipment, while classroom learning often fails to prepare individuals for real-world scenarios.
AR provides a safe and effective training ground. New employees can practice complicated tasks on a virtual machine in a controlled environment.
They learn proper operational steps and practice emergency shutdown procedures, building crucial muscle memory without risk to themselves or expensive equipment. This immersive learning helps people learn faster, retain more information, and become fully competent before stepping onto the production floor. Companies are increasingly exploring different augmented reality applications to create a more skilled and prepared team.
Choosing Your Tools: Mobile AR vs. Dedicated Headsets
Once you have identified a solid use case for augmented reality in your industry, the next step is selecting the appropriate hardware. This decision involves matching the right tool to the job, the environment, and the users. The two main options are mobile devices—smartphones and tablets—or purpose-built AR headsets.
Making the right choice from the start can prevent future complications and wasted investment. The best path depends on task complexity, the need for hands-free operation, budget, and the planned rollout strategy.
The Power and Accessibility of Mobile AR
For many companies, the easiest entry point into AR is through mobile devices. Most team members already own and know how to use smartphones and tablets. This reduces the learning curve and keeps initial costs down, making it ideal for tasks where a worker can spare a hand to hold a device.
Mobile AR is well-suited for several key scenarios:
- Field Service and Inspections: A technician can hold a tablet up to a machine to see live diagnostic data or pull up a digital manual.
- Quality Assurance Checks: An inspector can use their phone to overlay a digital blueprint onto a finished part, immediately spotting minor flaws or deviations.
- Simple Maintenance Tasks: For quick fixes or part identification, a phone or tablet provides sufficient AR power without specialized gear.
The widespread availability of these devices is fueling this trend. Mobile AR is one of the fastest-growing segments of the AR market, valued at around USD 37.73 billion and poised for massive growth. Its simplicity and portability are helping industries from automotive to aerospace modernize their operations. More details on the growth of the mobile AR market are available in recent reports.
When to Choose Dedicated AR Headsets
While mobile AR is highly accessible, some jobs require both hands to be free. This is where dedicated AR headsets, or smart glasses, become necessary. These devices place digital information directly in a worker's line of sight, allowing for hands-free operation.
The key advantage of a headset is that it integrates digital information seamlessly into a person's natural workflow. A mechanic does not have to stop, pick up a tablet, find the right page, and put it back down. The information is simply there.
This hands-free capability is a game-changer for critical, high-value tasks:
- Complex Assembly: For intricate builds, a headset can project holographic, step-by-step instructions onto the assembly, guiding a worker without breaking their focus.
- Remote Expert Assistance: A field technician wearing a headset can repair critical equipment while an expert back at the office sees their exact view and provides real-time annotated guidance.
- Surgical Maintenance Procedures: For delicate work demanding absolute precision, AR headsets keep vital stats and guides in the user's peripheral vision, boosting accuracy and reducing the mental load of remembering each step.
Your Roadmap to Implementing an AR Strategy

Adopting augmented reality for industry is a fundamental shift in how work gets done, not just a technology purchase. Without a solid plan, even the most promising AR projects can fail. This roadmap breaks the process into practical, manageable steps to guide your organization from an initial idea to a powerful, enterprise-wide tool.
The journey should begin with a single, carefully chosen pilot project. This allows you to demonstrate real value quickly, gain buy-in, and learn crucial lessons before scaling up.
Identify a High-Impact Pilot Project
Your first goal is to achieve a quick, decisive win. Look for a problem where AR can make an immediate, undeniable impact. Focus on tasks that are notoriously slow, error-prone, or require extensive training.
Start by asking the right questions:
- Where are our biggest operational bottlenecks?
- Which tasks generate the most rework or fail quality control checks?
- What processes tie up our most senior experts?
- Where are the highest risks for injury or expensive equipment damage?
The best pilot projects are often in complex assembly, field service repairs, or detailed quality inspections. These areas offer clear metrics—such as faster completion times or fewer mistakes—making it easy to prove the technology’s value.
Build a Compelling Business Case
Once you have a target, you need a business case that speaks the language of leadership: ROI. This is where you move beyond the "wow factor" of AR and focus on hard numbers. Your calculations must be rooted in your own operational data.
A strong business case does not just promise improvements; it quantifies them. Tally the real cost of the current problem—in wasted hours, scrapped materials, and machine downtime—and then project exactly how AR will reduce those costs.
For example, if a specific repair typically takes a technician eight hours, and an AR remote assistance tool reduces that to four, you have a direct labor saving. If that same repair usually requires flying in an expert, you can add those travel costs to your savings. Presenting these concrete figures is what gets an investment approved.
Select the Right Partners and Technology
Choosing the right technology vendor is as critical as selecting the right hardware. You need a partner who understands industrial settings and can help integrate the AR solution with your existing systems, such as your ERP or MES. This integration is key to pulling real-time data into the AR experience.
Content creation is equally important. The digital instructions and 3D guides must be intuitive and easy to follow. Look for a provider who can help you transform existing CAD files and technical manuals into engaging, interactive content. The best solutions often depend on a strong backbone, as AI-powered XR needs more than algorithms to perform reliably at scale.
Train Your Workforce and Scale Your Initiative
Great technology is useless if people do not use it. A successful rollout requires a smart training and change management plan. Start with a small group of "champions"—individuals who are enthusiastic about the technology. Let them become masters and then empower them to train their peers.
This "train-the-trainer" model fosters organic buy-in and helps overcome skepticism. As your pilot project achieves success, use those results to build momentum. The data from your first success becomes the foundation for every subsequent business case.
From there, you can scale your AR strategy step-by-step:
- Standardize Workflows: Take what you learned from the pilot and create standardized AR-guided procedures for other similar tasks.
- Expand Use Cases: Move from maintenance to assembly, or from assembly to training, applying the technology to solve new problems across the facility.
- Integrate Deeper: Connect your AR platform to more data sources, like IoT sensors on your machinery, to create a richer, more context-aware experience for your workers.
By following this roadmap, you can introduce augmented reality into your operations strategically, ensuring each step builds on the last and delivers real, measurable value.
What's Next for AR in Industry?
Augmented reality is becoming a core component of the modern industrial ecosystem. Its future lies in its deep integration with other Industry 4.0 technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and digital twins.
When these technologies work together, they create a smarter, more predictive factory environment.
Imagine an IoT sensor on a critical pump detecting a minor vibration, an early sign of a future breakdown. Instead of just triggering an alert, this signal immediately notifies the closest technician. Simultaneously, an AI analyzes the data, pinpoints the likely fault, and sends the appropriate AR repair guide to that technician's smart glasses.
When they approach the pump, they see a digital overlay pointing out the exact part to replace, with holographic instructions guiding them through every step.
A Shift to Predictive Operations
This synergy transforms maintenance from a reactive process into a proactive, predictive strategy. AR becomes the human-friendly interface for the vast streams of data from a connected factory.
- Connecting with IoT: A worker can glance at a machine and, through their AR glasses, see its live temperature, pressure, and output data overlaid on it.
- Insights from AI: AI works in the background, analyzing data to flag potential issues and suggest process improvements, which AR delivers as clear, actionable steps.
- Practicing with Digital Twins: Before touching a wrench, a technician can run through a complex repair on a machine's virtual "digital twin" using AR, ensuring the real job is done perfectly the first time.
This represents a massive leap forward to an environment where data drives action. AR ensures that action is fast, precise, and effective, reducing downtime and boosting output.
The financial impact is significant. The global AR market was valued at approximately USD 31.97 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 88.4 billion by 2026. Collectively, AR and VR are expected to add a staggering USD 13 trillion to the global economy by 2030.
To learn more, you can explore detailed forecasts on AR's future economic impact. These figures show that AR is a core component of any serious, long-term digital strategy.
Got Questions? We've Got Answers
Adopting augmented reality for industry is an exciting prospect that naturally raises questions. Here are answers to some of the most common inquiries from leaders planning their AR strategy.
This section serves as a quick-reference guide to help you overcome common hurdles and move forward with confidence.
What Kind of ROI Can We Actually Expect from an AR Project?
The ROI depends on the specific application, but the returns are almost always tangible. Most companies see a significant return by focusing on clear business metrics, such as reduced machine downtime, faster assembly, and fewer errors.
For example, using AR for remote assistance can immediately eliminate the travel costs of sending an expert to a site—a direct, measurable saving from day one. In other cases, using AR to guide workers through complex assembly has been shown to reduce rework costs by as much as 90% and cut training time in half. The key is to start with a pilot project that solves a real, quantifiable problem.
Do We Need a Team of Developers to Create AR Content?
Not anymore. While this was once a major barrier, modern AR platforms are designed for the people who do the work. You do not need to be a programmer to create powerful AR instructions.
Many of these tools are "no-code" or "low-code," enabling your own subject matter experts—the senior engineers and veteran technicians who know your equipment best—to build the guides themselves. They can drag and drop existing 3D CAD files, add notes, and overlay videos where needed. While a highly customized application might still require specialized help, creating standard operating procedures or training guides is well within the capabilities of your current team.
The purpose of modern industrial AR platforms is to empower your experts to digitize their own knowledge, making the process faster, more cost-effective, and easier to scale.
What are the Biggest Hurdles in a Successful AR Rollout?
The technology is rarely the most difficult part. The primary challenges are typically related to people and processes. A successful AR rollout depends more on a smart change management plan than on the software itself.
Common hurdles include:
- Getting Buy-In: Change can be intimidating. Some team members may be hesitant to adopt a new way of working. The best approach is to involve them from the start, demonstrate how the technology makes their job easier, and identify enthusiastic "champions" to lead the initiative.
- Siloed Systems: AR delivers the greatest value when it integrates with other business systems, like your MES or ERP. As a standalone tool, its impact will be limited. Planning for integration is key.
- Fuzzy Goals: Starting a project without a clear problem to solve is a recipe for failure. You must define what success looks like from the beginning with hard metrics to prove its value.
Addressing these human factors in advance is what distinguishes a successful pilot project from a full-scale, enterprise-wide AR implementation.
Ready to see how AR can directly impact your operational efficiency and training outcomes? AIDAR Solutions provides specialized AR and VR applications that deliver measurable results, from halving service times to accelerating employee learning. Explore our solutions at https://aidarsolutions.com.



Comment(01)