Augmented Reality Manufacturing Guide
Picture this: a factory floor where digital work instructions hover in mid-air right over the equipment they relate to. Imagine new technicians tackling complex repairs with the calm precision of a 30-year veteran. This isn't a scene from a sci-fi movie. It's what’s happening today with augmented reality in manufacturing.
AR technology closes the gap between digital blueprints and the physical world. It superimposes computer-generated images, 3D models, and live data directly onto a worker’s view of their surroundings.
How AR Is Reshaping the Modern Factory Floor

At its heart, AR changes how people interact with their work environment. Instead of referencing a thick paper manual or a static monitor across the room, an operator sees critical information right in their line of sight, usually through smart glasses or a tablet.
Think of it as having an intelligent, dynamic guide providing visual cues at the exact moment you need assistance. This transforms even the most complicated jobs into a series of straightforward, guided steps, which is a game-changer for consistency and quality.
The Bridge Between Digital and Physical Worlds
AR acts as the crucial interface between a factory’s “digital twin”—the virtual replica of all its processes and machines—and the actual, hands-on work happening on the floor. It’s this connection that empowers the workforce, turning abstract data into actionable visual cues.
For instance, an assembly worker doesn't need to decipher a complex schematic. They can see a holographic overlay showing them exactly where to place a component and in which orientation.
This direct visualization solves some of the most stubborn problems in the industry. It’s a practical tool for:
- Simplifying Complexity: AR breaks down intimidating assembly or maintenance jobs into simple, visual steps that are easy to follow.
- Improving Accuracy: By highlighting the correct parts and tools for the job, it dramatically cuts down on human error.
- Accelerating Learning: New hires can get up to speed in a fraction of the time with on-the-job, in-context guidance.
By merging digital insights with the physical environment, AR enhances training, maintenance, and quality control, offering operators real-time contextual information to streamline complex processes and drive operational efficiency.
More Than Just a Display
The impact of augmented reality in manufacturing goes beyond simply showing instructions. Modern AR systems can interface with other connected tools on the floor, creating a smarter, more interactive workspace.
An AR headset, for example, could sync with a smart torque wrench and display a green confirmation in the worker's vision when a bolt is tightened to the perfect specification. No guesswork is needed.
This level of integration fosters a more intuitive and responsive work environment. It reduces the mental strain on employees, freeing them to focus on the quality of their work instead of juggling different sources of information. This shift is fundamental to building a more skilled, resilient, and efficient team—and it's paving the way for a new era of industrial productivity.
The Real-World Payoff: AR's Key Benefits on the Factory Floor

Bringing augmented reality to the factory floor is about delivering tangible, measurable results that tackle the everyday challenges of manufacturing—efficiency, quality, training, and safety. This is where AR stops being a buzzword and starts becoming a powerful tool for operational excellence.
When AR overlays digital information, like instructions or 3D models, directly onto a worker's view of the physical world, it provides instant, in-context guidance that empowers people to do complex jobs faster and more accurately. It’s no surprise that the manufacturing sector is a key driver of the growing AR market, all thanks to these practical, value-driven applications.
Driving Unprecedented Operational Efficiency
One of the most immediate benefits of augmented reality manufacturing is a significant leap in efficiency. Consider traditional workflows: a worker stops what they're doing, walks to a terminal or flips through a binder, memorizes the next step, and then returns to the task. This process is filled with friction, creating opportunities for delays and mistakes.
AR eliminates that friction. With AR-guided assembly, step-by-step instructions appear directly in the worker's line of sight. It's a hands-free, heads-up approach that fosters confidence and speed. In fact, studies show AR can reduce task completion times by 25-50%. That is a serious productivity gain that flows directly to the bottom line. This boost is a core reason augmented reality for manufacturing has become so compelling.
Drastically Reducing Errors and Rework
Every manufacturer understands the cost of rework. It’s a drain on time and materials, often stemming from human errors like grabbing the wrong part or assembling something in the wrong sequence. AR acts as a real-time quality control expert, preventing these mistakes before they happen.
Imagine visual overlays that highlight the exact bin to pick from, show the correct orientation for a part, and then provide a "green light" confirmation once it's placed properly. This live validation makes it incredibly difficult for an operator to make a mistake.
By providing in-the-moment verification, AR systems can reduce assembly errors by up to 90% compared to traditional paper-based instructions. This not only slashes scrap and rework costs but also elevates overall product quality and consistency.
Accelerating Training and Upskilling the Workforce
The skills gap is a persistent challenge in manufacturing. Getting new hires proficient on complex machinery is often a slow, resource-intensive process. AR changes the dynamic by turning the factory floor itself into an interactive training environment.
New employees can put on AR glasses and receive on-the-job guidance from a "digital mentor" that shows them exactly what to do, step-by-step. They build real-world competence from day one, tackling complex jobs weeks or even months sooner than with traditional training methods.
This approach also helps capture the invaluable knowledge of experienced veterans and makes it available on-demand for the entire team. Taking it a step further, integrating concepts from gamified learning for professional development can make this training even more engaging and effective.
Enhancing Worker Safety Protocols
A safe work environment is paramount, and AR brings a new layer of proactive risk management to the factory floor. The technology can be programmed to recognize and flag potential hazards before an incident occurs.
For example, an AR system could:
- Identify Hot Surfaces: Display a glowing red overlay on machinery that is too hot to touch.
- Mark High-Voltage Areas: Create a clear visual boundary around dangerous electrical panels.
- Guide Proper Procedures: Ensure critical safety protocols, like lockout/tagout, are followed in the exact required sequence.
By making invisible dangers visible, AR helps prevent accidents. It reinforces best practices and builds a stronger, more resilient culture of safety across the entire facility.
To tie it all together, let’s look at how these benefits play out across different departments on the factory floor.
AR Benefits Across Manufacturing Functions
This table summarizes how augmented reality delivers specific, measurable improvements in key manufacturing areas.
| Manufacturing Function | Challenge Without AR | Solution With AR | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assembly & Production | High error rates from manual checks; slow task completion. | Step-by-step visual instructions; real-time validation. | Up to 90% error reduction; 25-50% faster assembly. |
| Quality Control | Inconsistent inspections; reliance on paper checklists. | Digital checklists; automated defect detection overlays. | Improved accuracy; standardized inspection process. |
| Training & Onboarding | Slow learning curve; dependence on senior staff for help. | On-the-job guided learning; "see-what-I-see" remote support. | 30-50% reduction in training time; faster skill acquisition. |
| Maintenance & Repair | Complex procedures from manuals; long machine downtime. | Remote expert assistance; 3D models of internal parts. | Faster diagnostics and repair; increased equipment uptime. |
Ultimately, AR isn't just one solution; it's a versatile platform that strengthens the core functions of any manufacturing operation, from the assembly line to the maintenance bay.
Where AR Gets Real: Practical Uses in Modern Manufacturing

The true power of augmented reality comes into focus when you see it solving real, everyday problems on the factory floor. This is where augmented reality manufacturing stops being a concept and becomes a game-changing operational tool. AR isn’t about replacing skilled workers; it’s about giving them digital tools right when they need them most.
By overlaying digital information onto physical tasks, AR turns complicated processes into simple, guided workflows. Let's dig into a few of the most impactful ways this technology is already making a difference.
Guiding Hands Through Complex Assembly
Imagine an aerospace technician assembling a highly complex piece of equipment with hundreds of parts, a dizzying sequence of steps, and zero room for error. A single mistake could mean thousands in rework or a critical failure down the line. The traditional method involves constantly looking away to check a PDF on a laptop or flip through a massive paper binder, breaking concentration and inviting mistakes.
Now, let's replay that with AR. The same technician puts on a pair of smart glasses. As they look at the main chassis, a 3D hologram of the next part appears, hovering in the exact spot and orientation it needs to be installed.
- Step-by-step visuals walk them through every single action, eliminating guesswork.
- Part verification is integrated. The system can highlight the correct parts bin, making it nearly impossible to grab the wrong component.
- Instant feedback confirms when a bolt is torqued correctly, displaying a green checkmark in the technician's view.
This hands-free, heads-up workflow keeps the technician focused, leading to a massive boost in both speed and accuracy. Studies show that AR-guided assembly can reduce errors by up to 90%, ensuring the job gets done right the first time.
By turning dense schematics into interactive, 3D instructions, AR-guided assembly gives operators the confidence to tackle intricate tasks with precision. It effectively turns every worker into an expert.
This isn’t just about boosting productivity; it’s about standardizing quality across your entire team, regardless of individual experience levels. The ability to visually guide workers through complex procedures is one of the most compelling augmented reality industrial applications available today.
Getting Expert Help, Instantly and Remotely
Picture this: a critical machine on a remote production line goes down. Every minute of downtime costs thousands of dollars. The on-site technician is new and doesn't know how to diagnose the complex electrical problem. The only senior engineer who knows this machine inside and out is working from an office hundreds of miles away.
Traditional options are inefficient: fly the expert in (a day or more of downtime) or attempt to resolve the issue over a confusing phone call.
With AR, the fix can be immediate. The on-site technician puts on their smart glasses and starts a remote assistance call. The senior engineer sees exactly what the technician sees, in real-time, from their own desk.
From there, the engineer becomes a virtual co-pilot:
- They can annotate the real world. The expert can circle a specific valve or draw an arrow pointing to a hidden switch, and those annotations appear locked onto the physical machine in the technician's view.
- They can share schematics. The expert can push a wiring diagram or technical manual directly into the technician's field of view.
- They can demonstrate the fix. Using their own hands, they can show a procedure, which appears as a ghost-like overlay for the technician to copy.
This "see-what-I-see" support dramatically reduces repair times, in some cases cutting machine downtime by over 50%. It’s a way to distribute the knowledge of your most valuable experts to anyone, anywhere, anytime.
A New Era for Quality Control and Inspection
Quality control is another process well-suited for an AR upgrade. An inspector's job demands a sharp eye and strict adherence to specifications. Traditionally, this means constantly comparing a finished part to a 2D drawing or a CAD model on a separate screen—a slow process that is open to human error.
Now, imagine that inspector holding an AR-enabled tablet. They point its camera at a newly made part. Instantly, a perfect digital 3D model is overlaid directly on top of the physical object.
Any flaws—misalignments, missing holes, incorrect dimensions—are immediately obvious where the digital model and the real part do not align. The system can even flag these spots in red automatically, making defect detection fast and nearly foolproof. The inspector can then capture an image and add notes directly in the AR application, creating a perfect digital record for the quality team. This approach not only makes inspections up to 40% more accurate but also builds a consistent, standardized quality process for the entire operation.
Choosing the Right AR Solution for Your Operations
Getting augmented reality right isn't about chasing the flashiest new gadget. It’s about picking the right tools for the job. The success of any augmented reality manufacturing project comes down to a thoughtful choice of both hardware and software. Each piece has to fit your specific needs, whether that’s on a fast-moving assembly line or in a meticulous quality control lab.
Making the right decision means understanding the entire technology stack. You need to consider how a device will feel after an eight-hour shift and how smoothly your new software will integrate with the systems you already depend on. This section provides a clear framework to navigate these choices so your investment pays off.
Matching the Hardware to the Task
The device a worker uses is their window into the augmented world, and one size does not fit all. The hardware you choose has a direct impact on whether your team adopts the technology and how effective it is. The goal is simple: give your team a tool that makes their job easier, not more complicated.
Three main types of AR hardware are used in manufacturing, each with its own strengths for different jobs.
- Smart Glasses: These are the go-to for hands-free work. Technicians performing complex assembly or maintenance can follow instructions in their line of sight without ever needing to look away. This is where AR becomes truly immersive and keeps workers in their workflow.
- Tablets and Smartphones: With their large screens and familiar interfaces, these handheld devices are perfect for quality control, inspections, and any situation where someone needs to access detailed information. They are versatile, relatively affordable, and a great entry point into AR.
- Projectors: For stationary work, projection-based AR can beam instructions or guides directly onto a workbench or the product itself. This is a game-changer for training stations or standardized assembly cells where multiple people perform the same task repeatedly.
Picking the right device is as much about ergonomics as it is about function. An assembly line worker needs a lightweight, hands-free headset. A quality inspector, on the other hand, gets more value from the detailed view and interactive screen of a tablet.
The momentum is clearly heading toward hands-free solutions. The number of AR smart glasses shipped to the manufacturing sector is expected to hit a staggering 27 million by 2025, proving that a heads-up, hands-free approach is what frontline workers need.
A quick look at the hardware shows there's a clear trade-off between mobility, field of view, and how you interact with the information.
AR Hardware Comparison for Manufacturing Tasks
| Hardware Type | Primary Use Case | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Glasses | Complex assembly, remote assistance, maintenance | Hands-free operation, keeps user focused | Smaller field of view, can be costly |
| Tablets & Smartphones | Quality control, inspections, documentation | Large screen, familiar interface, affordable | Requires one hand, can be dropped or damaged |
| Projectors | Stationary assembly, training stations | Shared view for collaboration, no wearables | Limited to a fixed location, requires setup |
As you can see, the "best" device is entirely dependent on the specific task your team needs to accomplish.
Critical Software Considerations
Hardware might be the most visible part of the equation, but the software is the engine that drives it. Your AR platform must be more than a simple viewer; it needs to integrate into your factory's digital backbone. Choosing the right software is what separates a pilot project from a full-scale, value-driving deployment of augmented reality manufacturing.
When you're evaluating software platforms, focus on these three areas to ensure you're set up for success.
- Seamless Integration: Can it connect to your other systems? Look for platforms with robust APIs that connect to your Manufacturing Execution System (MES), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), and Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) tools. This is how you pull work orders, schematics, and other vital data directly into the AR experience, creating one reliable source of truth.
- Scalability and Content Management: How difficult is it to create and update your AR content? The best platforms allow you to build AR work instructions directly from your existing CAD models, which dramatically reduces authoring time. Your software should make it easy to manage and deploy these instructions to different teams, sites, and devices as your AR program expands.
- User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX): The interface must be simple for the person on the factory floor. A clunky or confusing UI will hinder adoption, no matter how powerful the technology. The whole point is to reduce cognitive load so workers can focus on the task, not on figuring out how to use the tool. Look for clean, straightforward designs that deliver information clearly.
By carefully matching the right hardware to each job and picking a software platform built to integrate and scale, you'll build a strong foundation for an AR program that truly makes an impact.
A Step-by-Step Framework for Implementing AR
Bringing augmented reality into your manufacturing environment requires a thoughtful, phased approach to manage risk, secure buy-in from your team, and build a foundation that can scale. A solid framework is what separates a flashy tech demo from a full-scale deployment that delivers real value.
The journey doesn't start with a massive, facility-wide overhaul. It begins with a single, well-chosen step.
Start with a High-Impact Pilot Project
The quickest way to prove the value of augmented reality manufacturing is to solve a tangible problem. Pinpoint a specific pain point in your operations—perhaps it’s a complex assembly process riddled with errors or a maintenance task that always causes a bottleneck. A focused pilot project lets you demonstrate ROI quickly and builds momentum.
Pick a use case where success is easy to measure. This gives you hard data to build a compelling business case for a broader rollout. A successful pilot is your best internal marketing tool, turning skeptics into supporters.
Engage Your Workforce Early and Often
Technology is only as good as the people using it. Involve your frontline workers from day one. They have invaluable insights into daily operations and can immediately spot where AR could make the biggest difference. Their early feedback is critical for designing a user experience that genuinely makes their jobs easier, not more complicated.
Fostering a culture of collaboration and open communication is essential for adoption. When employees see AR as a tool that empowers them rather than replaces them, they become active participants in its success.
This engagement also helps you refine your training. Using AR to onboard new hires is a powerful strategy, and you can get a deeper look at this approach in our guide on augmented reality for training.
This visual shows a common workflow where AR overlays digital models on physical equipment, gives assembly guidance, and helps with quality checks.
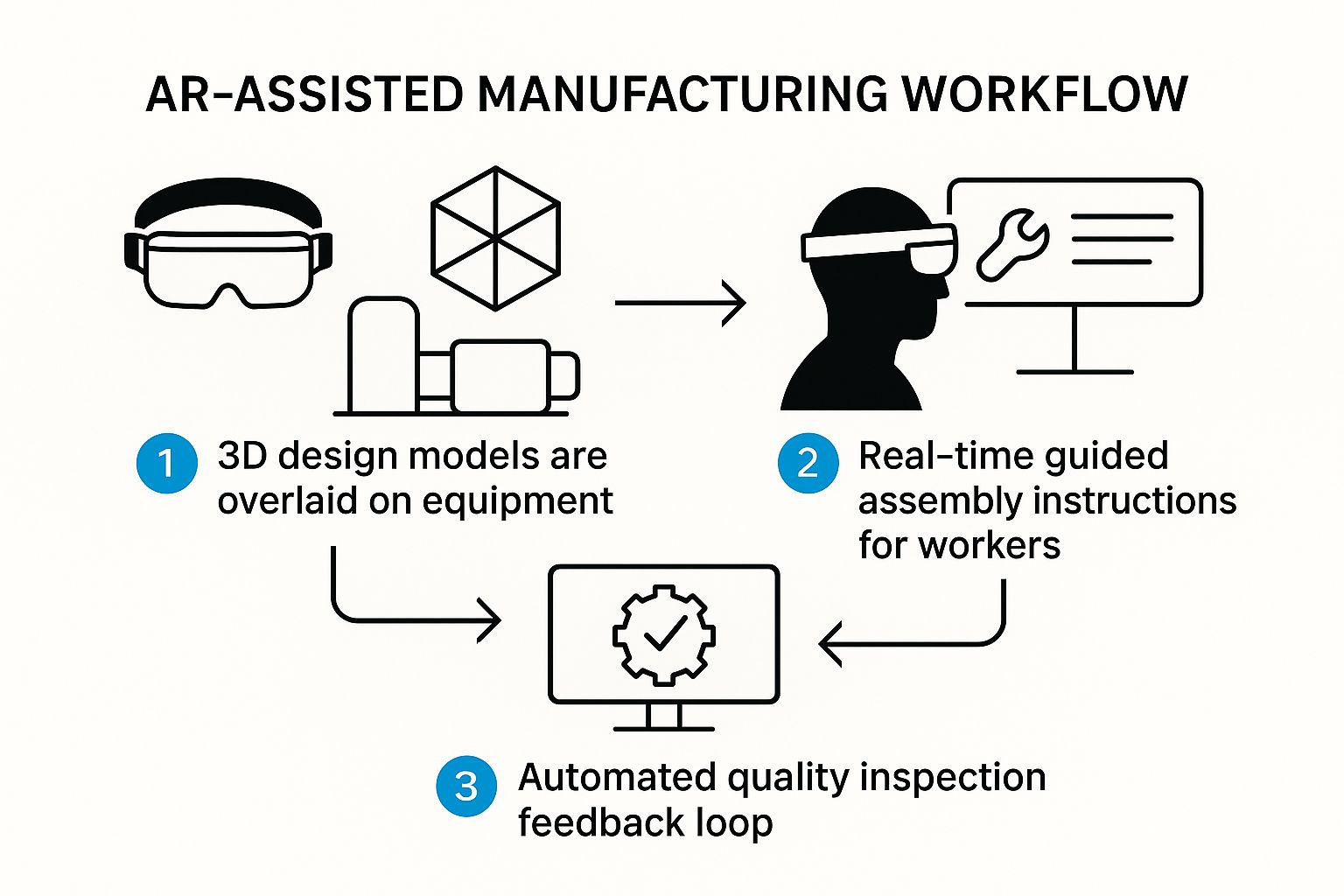
You can see how AR creates a closed loop, guiding the worker through a task and then validating the result in one fluid process.
Select the Right Technology and Partners
Once you have a successful pilot under your belt and an engaged team, it’s time to think long-term. Look for technology providers who understand the unique challenges of a factory floor. Your hardware and software have to be robust, scalable, and able to integrate with your existing systems like MES or PLM.
The global AR market is growing, driven by better hardware and smarter AI, making the technology more powerful and practical for industrial settings. Advanced content creation techniques are also a game-changer; for instance, the ability to convert text to 3D models can dramatically speed up how you populate your AR environment with digital assets.
Measure, Scale, and Optimize
Finally, you need to track your progress with clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Without them, it's impossible to measure success.
- Efficiency Gains: Are assembly times decreasing? Are tasks being completed faster?
- Quality Improvements: Track the reduction in errors, scrap, and rework.
- Training Effectiveness: How quickly are new hires reaching full productivity?
- Safety Records: Are you seeing fewer workplace incidents in AR-assisted areas?
Use this data to justify a wider, more strategic rollout. Keep gathering feedback from your teams to fine-tune workflows and identify new opportunities. This ensures your augmented reality manufacturing program keeps evolving and delivering value for years to come.
Common Questions About AR in Manufacturing
When considering a new technology for the factory floor, key questions always arise. What will it cost? How hard is it to implement? And will my team use it? These are the make-or-break factors for any investment.
With augmented reality manufacturing, these concerns are front and center. Let’s tackle the most common questions and provide the straightforward answers you need to see the real potential of AR.
What Is the Typical ROI for an Augmented Reality Manufacturing Project?
The Return on Investment (ROI) for AR is driven by concrete improvements in how work gets done. Most companies realize a return on their investment within 12-18 months after a well-planned rollout.
This ROI comes from a few key wins:
- Fewer Mistakes: When operators have visual instructions directly in their line of sight, errors plummet. That means less scrap, less rework, and a direct reduction in material and labor costs.
- Faster Training: Long, drawn-out onboarding is a thing of the past. New hires can be guided by AR from day one, making them productive in a fraction of the usual time.
- Quicker Fixes: In maintenance, every minute of downtime is costly. AR helps technicians diagnose and fix problems faster, getting equipment back online.
An AR-guided assembly process can boost a single worker's efficiency by 25-50%. The best way to calculate your potential ROI is to benchmark your current metrics—like average assembly time or first-pass yield—and then measure the improvement after implementing AR.
AR is not just a technology expense; it is a strategic investment with a clear, predictable payback.
How Difficult Is It to Integrate AR with Our Existing Factory Systems?
This is a major consideration. No one wants a tool that operates in a silo, disconnected from other systems. Modern AR platforms are designed to integrate with the systems you already have.
The complexity depends on your current IT infrastructure and the AR software you choose. Enterprise-grade AR platforms come with robust APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that act as bridges to your other systems, like:
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
A common and effective integration is pulling work orders directly from an MES and converting them into interactive AR instructions. This creates a single source of truth and reduces confusion on the floor. It requires collaboration between your IT and operations teams, and a good AR provider will have a team to help ensure a smooth process.
Our advice? Start with a focused pilot project. It’s the perfect way to work out any integration issues on a small scale before a full deployment.
Do Our Workers Need Extensive Training to Use AR Devices?
This is where many are surprised. The answer is a resounding no. In fact, one of the biggest benefits of augmented reality manufacturing is how intuitive it is. The purpose is to make complex jobs simpler, not to hand your team another complicated piece of technology to learn.
The user interface on a pair of smart glasses is often as simple as a smartphone app. Most workers get comfortable with it within a few hours—sometimes in a single shift. The on-screen guidance allows them to focus on the physical task, not on figuring out the tool. Our article on augmented reality remote assistance dives deeper into how this simplicity empowers technicians.
Time and again, the workforce adapts quickly and positively. When you provide people with a tool that makes their job easier and safer, they will use it. It’s not just about adoption; it’s about empowering your team.
Ready to stop asking questions and start getting answers with a real-world demonstration? AIDAR Solutions specializes in creating custom AR and VR applications that solve concrete manufacturing challenges. See how our expertise can drive efficiency, quality, and safety in your operations by visiting us at https://aidarsolutions.com.


